Posted on:
Modified on:
Matthew 5:17 (ESV)
[17] “Do not think that I have come to abolish the Law or the Prophets; I have not come to abolish them but to fulfill them.
Most of us have been taught that “the Law” was a good thing in its time, but by “fulfilling” it, Jesus rendered it obsolete. He didn’t abolish it, but because it was a foreshadowing of His life, death and resurrection, it no longer has any function other than as a tutor, to teach us about sin. To most, more like an artifact in a museum.
But if “the Law” is obsolete, then so are other things based on it.
Judaism as an ethnic group goes back to Abraham, of course, but the one thing God gave them that allowed them to survive 2000 years of Diaspora was their distinctive identity as a people with an elaborate cultural heritage. If “the Law” is obsolete, then so is the heritage, and so, too, is the people. What then, is the purpose of the modern state of Israel? The late R.C. Sproul (who I nevertheless liked) echoed the sentiments of Reformed churches around the world in saying that it has no purpose whatsoever!
Exposition of the text
In this post I’m going to provide exegesis of the following passage, then discuss some of the consequences.
Matthew 5:17–19 (ESV)
[17] “Do not think that I have come to abolish the Law or the Prophets; I have not come to abolish them but to fulfill them. [18] For truly, I say to you, until heaven and earth pass away, not an iota, not a dot, will pass from the Law until all is accomplished. [19] Therefore whoever relaxes one of the least of these commandments and teaches others to do the same will be called least in the kingdom of heaven, but whoever does them and teaches them will be called great in the kingdom of heaven.
Most conservative Evangelical theologians, and almost all Dispensationalists, believe that the Mosaic Covenant, the “Law of Moses”, was conditioned on Israel’s continuous keeping of “the Law“. They say that when Israel rejected their Messiah, they forfeited this particular Covenant. One of the chief passages in the Bible used to support that opinion is Matthew 5:17, taken out of context and carelessly translated. Yet I think that, taken in context, it says the opposite.
In a recent exchange on Facebook with a person who is clearly a sophisticated student of the Bible (and a new friend of mine, as well), I responded to this statement:
In Matthew 5:17, Jesus says, “Do not think that I have come to abolish the Law or the Prophets; I have not come to abolish them but to fulfill them.” This statement indicates that Jesus’ mission was not to discard the Law but to bring it to its intended purpose. The Greek word used for “fulfill” (πληρόω, plēroō) suggests completion or bringing to full expression. Jesus lived in perfect obedience to the Law, thus fulfilling it in a way no one else could.
Mostly, that analysis is on track, but the final sentence reveals a fundamental misunderstanding of Jesus’ mission. It hinges on what is meant by “the Law” and is also a misstatement of what verse 17 actually says.
What is “The Law”?
I recall a weekday Men’s Bible study teacher asking the group what book of the Bible we would like for him to teach through next. I suggested Leviticus and got a kick out of all the dropped jaws and glazed eyes.
To most Christians, the idea of even reading Leviticus is daunting, let alone discussing its content in tedious detail. Leviticus is just… it’s…
…A cumbersome jumble of miscellaneous rules and regulations designed to show us the unmitigated evil of the human heart, and how ungrateful and hypocritical a people can be despite all God does for them.
But before we can “decode” our text, we need to agree on what “the Law” really is. When you see that term in the Old Testament, it is a translation of the Hebrew “Torah.” In the New Testament, it is a translation of the Greek “nomos.” Both words refer to the same thing. the problem is that the English word “law” doesn’t fit either of these foreign words very well.
Using a concordance
If you don’t speak Hebrew or Greek and you run across a word in one of these languages in the Bible, then the chances are you might look it up in a concordance. In the modern age, the best known and most used of these, for both languages, is Strong’s Exhaustive Concordance, but there are a number of others available. Strong’s introduced index numbers for the root form of each word found in the King James version. Newer concordances mostly use Strong’s index numbers, though there are additional numbering systems available.
Most concordances list English translations of the original word. In doing so, they may purport to serve the purpose of a dictionary, but it is important to realize that they are not dictionaries—they are indices! So, if Strong’s lists, for example, 25 uses of a single root word, it will generally break those down by the different ways that word has been translated. It isn’t telling you how it should be translated, but rather how it has been translated.
Fortunately, there are a number of actual translational dictionaries available, and many of those cross-reference the Strong’s index numbers.
Torah to a Jew
The Strong’s entry for Torah, H8451 on Biblehub.com, says “direction, instruction, or law.” A different edition of Strong’s, incorporated with the PocketBible Bible Study App, lists: “a precept or statute, especially, the Decalogue or Pentateuch—law.”
But to the faithful Jew, the “law” part of it is just a to-do list for living an orderly and God-pleasing life. “The 613 Habits of Highly Effective People“, so to speak. Torah to a Hebrew-speaking Jew means “teaching“—Instruction about who God is and what God does; and direction for how to lead family and community in the path God has paved.
But what specifically is “The Torah?”
That question has a lot of answers to a Jew, depending on context:
- First of all, it is of course the Five Books of Moses, called the Chumash (the five) by Jews and the Pentateuch by Hellenized Christianity.
- “Oral Torah” refers to a body of tradition handed down from generation to generation, beginning ostensibly with Moses. These are the “traditions of the elders” which Jesus condemned, but only to the extent that they occasionally conflicted with written Torah. Without question, Jesus and His disciples kept most of these customs themselves. These include ways of celebrating the Biblical feasts, celebration of additional, extrabiblical feast days, ritual washing customs, the entire body of blessings before meals and other activities, and much, much more. After AD 70, Pharisees and scribes assembled at Jamnia (Yavneh, modern Rehovot, between Tel Aviv and Ashdod) began the arduous task of writing down these previously oral-only traditions. The result is the Mishnah, and later two competing versions (“Babylonian” and “Jerusalem”) of the Talmud.
- In a much broader sense, anything that records the Word of God is also considered Torah. This includes the rest of the canonical Tanakh, or Old Testament. Messianic Jews, believers in Messiah Jesus, also include the New Testament in Torah.
But regardless of the dictionary definition, to a devout Jew, Torah reflects the way things are, not the way things are supposed to be.
Nomos to a Jew
Regarding the term “Law”, the New Testament uses the Greek nomos, following the lead of the Septuagint (LXX), the 2nd century BC Greek translation of the Old Testament that Paul used when taking his ministry to the Greek world. The LXX uses nomos for the Hebrew Torah because that was as close as the translators could come, grammatically.
Strong’s and NAS both define nomos as, “that which is assigned, hence usage, law.”
Thayer’s, as usual, gives a much more complete analysis:
(νέμω, nemo, to divide, distribute, apportion), in secular authors from Hesiod down, anything established, anything received by usage, a custom, usage, law.
Vine’s, my favorite language resource, says,
(νόμος, nomos), akin to nemo, “to divide out, distribute,” primarily meant “that which is assigned”; hence, “usage, custom,” and then, “law, law as prescribed by custom, or by statute.
An expanded view of Torah/Nomos
There is no denying that a significant part of Torah consists of legal precepts. In fact, by official Jewish count, there are 613 separate mitzvoth, or commandments, in the Five Books of Moses. These are contained in portions of Torah that are called Halachah, or “the way of walking.” As Paul would describe it, the part defining the proper “walk” of a Godly Jew.
The rest of Torah is called Aggadah, and it is the narrative part of Scripture. If Halachah is about expected behavior, Aggadah provides the rationale and motivation for that expectation. As expressed very eloquently by myjewishlearning.com, Jewish life is defined, not by “Law” or Halachah, but by the interplay between Halachah and Aggadah. “The interrelationship of Halakhah and Aggadah is the very heart of Judaism. Halakhah without Aggadah is dead, Aggadah without Halakhah is wild.”
My conclusion is that it’s only because of the legalism of 2nd Temple and Rabbinic Judaism and defensive translation/commentary by mostly antipathetic gentile scholars that both the Hebrew and Greek terms became associated exclusively with the strictly legal term, “law.”
What it isn’t
Starting probably with Augustine of Hippo, the Church developed a theory, now firmly entrenched in both Catholic and Protestant tradition, that “the Law” was composed of three parts: Moral Law, Civil Law, and Ceremonial Law. Supposedly, the Moral Law is still in force, but the Civil and Ceremonial Law have been annulled.
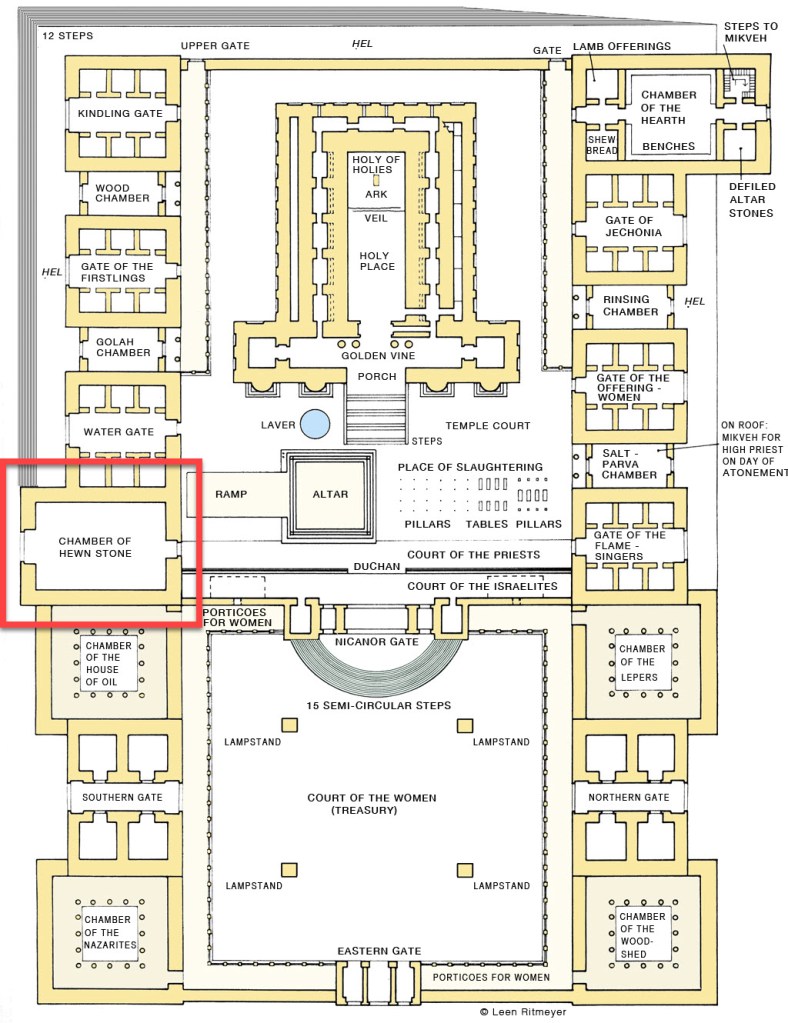
That tradition has absolutely no Biblical support and was never a part of prior Jewish belief. Furthermore, the view is theologically untenable, on several important levels. The Torah, or more accurately, Halachah, is a unified whole. To fail with respect to a single minor mitzvah is to fail with respect to all of Torah, no matter how you parse it. For more on this subject, see The Transfiguration and “Jewish Law”.
“The Law and the Prophets”
But Matthew 5:17 isn’t speaking about Torah alone, and certainly not Halachah alone. It mentions not just “the Law”, but rather, “the Law or the Prophets”, which was a common shorthand expression indicating the entire, Tanakh, or Old Testament. The Prophets didn’t establish any law. They proclaimed God’s judgements and revealed His plans for Israel and the World.
So, fully understood, verse 17 could not possibly be saying that Jesus “fulfilled the Law and the Prophets” merely by living in complete obedience to Halachah. Indeed, Jesus’ meaning is made perfectly clear by the very next verse: “[18] For truly, I say to you, until heaven and earth pass away, not an iota, not a dot [“jot and tittle” in KJV; “yodh or stroke” in the Hebrew alphabet], will pass from the Law until all is accomplished.“
As I sit here and gaze out my office window, I can clearly see that heaven and earth have not yet passed away. So, is God’s “Law” of less effect today than when Jesus spoke His Sermon on the Mount?
It happens to be Thursday as I start this paragraph, but I was sitting here typing last Saturday, too. I was violating the Jewish Sabbath in a number of ways. But I’m not Jewish, and I’m not bound by Jewish law. The Mosaic Covenant was between God and Israel, not between God and the Church (sorry, Reformed friends, they’re not the same), not between God and goyische God-Fearers (I just added a stub for a future post on non-Jewish pre-Christian believers), and not between God and all humanity. Has it passed away for Israel (whether they realize it or not)? I just checked again: the sun is still shining, the wind is still blowing, and squirrels are still running up and down the oak tree.
In case verse 18a was not enough, 18b adds even more punch: not the tiniest portion of “the Law” will pass until “all is accomplished“! All of what? All that is written in “the Law and the Prophets”. Aggadah as well as Halachah. All of God’s plans as revealed in the Old Testament. Some have, some have not. Jesus’ first advent has come and gone, but there is still a lot of prophecy unfulfilled. Some of my readers don’t believe in a Millennial Reign, but most believe in a coming final judgement. That is surely yet to come. Unfulfilled! The Law. The Covenants. None of that has passed away!
Other New Testament Uses of “Fulfill”
About the same time that I was participating in this discussion of Matthew 5:17–19 on Facebook, another man was independently taking the same stance as mine on another thread about the same subject. This man’s name is Dalton Mauldin, and he is the author of a book titled Finding the Way: A Scripture-Guided Journey to Break through Tradition to Find Truth, Faith, and a Closer Walk with God.
I am reading the book, and while Dalton and I aren’t on the same page on everything, we’re close enough to be Christian friends. In order not to reinvent the wheel, I have obtained his permission to quote him here as he discusses other instances of the term “fulfill” in the New Testament. This is an excerpt from his Chapter VIII:
“Then Jesus came from Galilee to the Jordan to be baptized by John. But John tried to deter him, saying, “I need to be baptized by you, and do you come to me?” Jesus replied, “Let it be so now; it is proper for us to do this to fulfill all righteousness.” Then John consented. (NIV)”
Did Jesus mean to “put an end to all righteousness”? Of course not! In this instance, “fulfill” was a translation of the same Greek word “pleroo.” It is clear in this usage that it does not mean “to put an end to” all righteousness, but more likely to demonstrate righteousness. It should also be noted that this is the same author, Matthew, who would likely use the word fulfill in the same way two chapters later.
In Romans 15:13, it says: “May the God of hope fill you with all joy and peace as you trust in him, so that you may overflow with hope by the power of the Holy Spirit. (NIV)”
In this instance, “fill” was translated from “pleroo” as well. It is clear in this usage that it does not mean “to put an end to”, but “to make full.”
In Colossians 1:25, Paul states: “I have become its servant by the commission God gave me to present to you the word of God in its fullness. (NIV)”
In this instance, “fullness” was translated from “pleroo” as well. It is clear in this usage that it does not mean “to put an end to” but means “in its entirety.”
In James 2:23 it says: “And the scripture was fulfilled that says, ‘Abraham believed God, and it was credited to him as righteousness,’ and he was called God’s friend. (NIV)”
In this instance, “fulfilled” was translated in the past tense of the word – you guessed it – “pleroo”. It is clear in this usage that it does not mean “to put an end to”, but to mean “brought into reality”.
In fact, there is no instance of “pleroo” translated as “to put an end to” or any similar meaning. Thus, “fulfill” cannot possibly mean anything that might resemble “put an end to.” Having eliminated the possibility of any meaning of “pleroo” that indicates an “end”, let’s look at the others: “to complete, to make full, to verify, to accomplish, to satisfy, and to preach fully”
A warning
If there is still any doubt about the permanence of “the Law”, Jesus then adds a stern warning for those who in any way would relax their observance of Torah:
Matthew 5:19 (CJB)
[19] So whoever disobeys [λύω, loo’-o, to relax, loosen, untie, break up, destroy, dissolve, melt, put off, contravene, annul] the least of these mitzvot and teaches others to do so will be called the least in the Kingdom of Heaven. But whoever obeys them and so teaches will be called great in the Kingdom of Heaven.
What about verse 20?
Matthew 5:20 (ESV)
[20] For I tell you, unless your righteousness exceeds that of the scribes and Pharisees, you will never enter the kingdom of heaven.
The ESV, NIV, NCV, NKJV and some other translations lump Matthew 5:17–20 under one subheading, such as “Christ Came to Fulfill the Law” in ESV. Others include the Salt and Light verses, 13–16 under the same subhead.
I think that it is bad exegesis to include verse 20 with the preceding verses, because rightfully verse 20 is an introductory verse to what follows, specifically Jesus’ discourse on the spirit of the 10 Commandments.
Regarding “the righteousness of the scribes and Pharisees,” this is a Hebrew play on words. צִדְקָה (tsidqah) is a noun that means “righteousness.” Jesus is teaching that righteousness means both the letter and spirit of Torah. Many scribes and Pharisees, though, had cheapened the term by using it to indicate simply “almsgiving alone.”
“Look at how righteous I am—I faithfully donate a shekel or two to widows and orphans.”
The conditionality of the Mosaic Covenant?
In my post, A Perspective on Biblical Covenants and Dispensations, I state my opinion that, despite contrary views, none of the Covenants with Israel were conditional—that each new Covenant built onto all of the previous Covenants. The Mosaic Covenant is still operative!
Matthew 5:17, is part of the justification for the disastrously mistaken idea that God is “done with the Jews”, either forever or until the Tribulation period. Do you think that’s a minority view among Christians? Wrong! It is a prominent teaching of the Catholic and Orthodox churches which dominate most of the world, as well as Reformed Protestant denominations, including Anglican, Presbyterian (my dad’s heritage), Lutheran (my mom’s heritage), and many denominations around the globe, many of which have the word “Reformed” in their name.
But even Dispensational denominations, which refuse to permanently write off Israel’s place in God’s plans for the last days, uniformly hold that the Mosaic Covenant is dead, because it was conditional.
There are two ways one can think of covenant “conditionality”:
- First, one can call a covenant “unconditional” if it makes promises (positive and/or negative) that one party is bound to keep no matter what the other party does or does not do, and “conditional” if the promises it makes are contingent on the actions of the other. In that sense, yes, the Mosaic Covenant is indeed conditional.
- But that is not what most Bible teachers mean when they say the Mosaic Covenant is conditional. They mean that its validity is conditional. “If you obey, I’ll bless you, if you disobey, I’ll curse you…” [That much is true—Deuteronomy 28 says it in no uncertain terms!] “…and if you keep disobeying, I’ll take my ball and go home!”
What triggered the supposed annulment of the Mosaic Covenant?
Many Dispensationalists will say that God cancelled the Mosaic Covenant when Israel, in the person of the Pharisees harassing Jesus (no doubt at the instigation of leadership in the Great Sanhedrin) rejected Jesus as messiah and blasphemed the Holy Spirit by attributing His miracles to Satan. This rejection, they say, is recorded in Matthew 12:
Matthew 12:22–25,30–32 (ESV)
[22] Then a demon-oppressed man who was blind and mute was brought to him, and he healed him, so that the man spoke and saw. [23] And all the people were amazed, and said, “Can this be the Son of David?” [24] But when the Pharisees heard it, they said, “It is only by Beelzebul, the prince of demons, that this man casts out demons.” [25] Knowing their thoughts, he said to them, “Every kingdom divided against itself is laid waste, and no city or house divided against itself will stand.
…
[30] Whoever is not with me is against me, and whoever does not gather with me scatters. [31] Therefore I tell you, every sin and blasphemy will be forgiven people, but the blasphemy against the Spirit will not be forgiven. [32] And whoever speaks a word against the Son of Man will be forgiven, but whoever speaks against the Holy Spirit will not be forgiven, either in this age or in the age to come.
The Dispensational scenario suggests that Jesus, at the beginning of his ministry, was actively preaching, demonstrating His power, and proclaiming his Messiahship, with the ultimate intention to rally the Land and establish the prophesied Messianic Kingdom. Paradoxically, the same people who teach this are also prone to teach that Jesus’ first advent was specifically intended to present Him as a suffering servant, not a military leader. As a result of the Pharisees’ rejection in Matthew 12, Jesus, in verse 32, (again in this scenario) announced that the scribes and Pharisees as representatives of Israel had committed an unpardonable national sin, so the Kingdom would be indefinitely delayed. From that day on, Jesus would no longer seek to win over the current generation but rather would concentrate on training His disciples and by extension their successors to carry His message to a far future generation. As a result, His miracles were henceforth done in relative privacy, His messages were delivered in parables that could only be understood by His “insiders”, and on His death, the Mosaic Covenant was cancelled and replaced by the New Covenant. Some say that “it is finished” uttered on the cross marks the instant of replacement.
I find that scenario to be deeply flawed and insupportable.
In my Covenants and Dispensations post, I point out that Christianity is more or less divided into two camps:
- The Covenantalists, who believe that Jewish Old Testament Israel was the original “Church”, and that the mostly gentile New Testament Church is the current and forevermore “Spiritual Israel”, and that there will be no Rapture or Millennial Reign.
- The Dispensationalists, who believe that Israel and the Church are distinct entities, and that the Church will be Raptured followed by a Millennial Reign during which Israel will finally accept their Messiah.
Almost all Christian denominations and local churches fall into one of those two camps. You can more or less recognize them by whether they practice infant baptism (Covenant), or believer’s baptism (Dispensational). Personally, I totally reject the majority Covenantal viewpoint. I do hold to the Dispensational views as shown by the bullet above, but I reject the concept of “dispensations” and the Dispensational belief that the Mosaic Covenant is dead.
Old Testament references to the New Covenant
That the New Covenant would replace the Old is not stated anywhere in the Old Testament. Several references do indeed predict that the “New Covenant” will be better than the “Old Covenant”, i.e., the Mosaic:
- Moses himself, in Deuteronomy 29:[4] (CJB), said, “to this day ADONAI has not given you a heart to understand, eyes to see or ears to hear!”. Though he does not mention a New Covenant, he goes on, in chapter 30, to describe times of apostacy and exile for Israel, followed by, in chapter 31, promises of restoration. Notable in this passage is,
Deuteronomy 30:5–8 (ESV) emphasis mine
[5] And the LORD your God will bring you into the land that your fathers possessed, that you may possess it. And he will make you more prosperous and numerous than your fathers. [6] And the LORD your God will circumcise your heart and the heart of your offspring, so that you will love the LORD your God with all your heart and with all your soul, that you may live. [7] And the LORD your God will put all these curses on your foes and enemies who persecuted you. [8] And you shall again obey the voice of the LORD and keep all his commandments that I command you today.
Only verse 5 here yet been fulfilled for the nation of Israel. Note that verse 6 concerning Israel’s heart is language characteristic of the New Covenant, but if the New cancels the Old, then why is it that that Israel will still “keep all His commandments that I command you today”—clearly speaking of “the Law of Moses.”
I have written a post recently dealing with Paul’s writings on this subject, in his epistle to the Romans: Yetzer, Yotzer and “The Law” in Romans 7:1–6.
- The best known of the New Covenant prophecies is found in,
Jeremiah 31:31–34 (ESV) emphasis mine
[31] “Behold, the days are coming, declares the LORD, when I will make a new covenant with the house of Israel and the house of Judah, [32] not like the covenant that I made with their fathers on the day when I took them by the hand to bring them out of the land of Egypt, my covenant that they broke, though I was their husband, declares the LORD. [33] For this is the covenant that I will make with the house of Israel after those days, declares the LORD: I will put my law within them, and I will write it on their hearts. And I will be their God, and they shall be my people. [34] And no longer shall each one teach his neighbor and each his brother, saying, ‘Know the LORD,’ for they shall all know me, from the least of them to the greatest, declares the LORD. For I will forgive their iniquity, and I will remember their sin no more.”
But this also is a Covenant with “the house of Israel and the house of Judah” and it too, in its context (read the entire chapter!), speaks of the acharit hayamim, the “end of days.” At least as it applies to national Israel.
- Ezekiel also repeats the prophecy, and once again the context places it firmly in the future, yet to be fulfilled.
Ezekiel 36:24–28 (ESV)
[24] I will take you from the nations and gather you from all the countries and bring you into your own land. [25] I will sprinkle clean water on you, and you shall be clean from all your uncleannesses, and from all your idols I will cleanse you. [26] And I will give you a new heart, and a new spirit I will put within you. And I will remove the heart of stone from your flesh and give you a heart of flesh. [27] And I will put my Spirit within you, and cause you to walk in my statutes [בְּחֻקַּי֙, bə·ḥuq·qay, “in my statutes”] and be careful to obey my rules [וּמִשְׁפָּטַ֥י, ū·miš·pā·ṭay, “and my ordinances/judgements”]. [28] You shall dwell in the land that I gave to your fathers, and you shall be my people, and I will be your God.
Once again, the New Covenant will ultimately renew Israel’s faithfulness to the Old Covenant, not replace it.