Posted on:
Modified on:
In Genesis 1:1–5, Day 1 and a number of earlier posts I presented a case for Old Earth Creationism and why I believe that Genesis 1 can only be interpreted as a visionary prophetic revelation, not a historical account.
In my most recent post, Moshe’s Week of Dreams, I presented a hypothesis as to why Genesis 1 reads as it does, presenting a 6-day creation process, beginning with light, and building to a description of the cosmos that matches what ancient peoples imagined it to be, a flat, floating island earth protected from the ocean above by a dome, under which reside the sun, moon and stars. All of us would agree that this description doesn’t match what we observe today.

Interpreting Genesis 1 as visionary and not literally descriptive begs the question: What about the rest of prehistoric Genesis, i.e., Genesis 2:1–11:9?
Well, in my view it is all prophetically revealed, but it is not clear to me that any of it is visionary, or that much of it is even non-literal. Prophecy can reveal truth in subtle and symbolic ways, or it can show truth directly.
My own interpretations of prophecy make use of the so-called “Golden Rule of Biblical Interpretation”:
“When the plain sense of Scripture makes common sense, seek no other sense; therefore, take every word at its primary, ordinary, usual, literal meaning unless the facts of the immediate context, studied in the light of related passages and axiomatic and fundamental truths, indicate clearly otherwise.”
–Dr. David L. Cooper (1886-1965),
founder of The Biblical Research Society
If you aren’t a theology buff like me, you may not have heard of this particular Golden Rule outside of my blogs. Something very similar that you probably have heard of in high school science classes is called Occam’s Razor. Its actual wording is, “entities should not be multiplied beyond necessity”, meaning that, if you are faced with several alternative solutions to a problem, always start out with the simplest; or, alternatively, the one requiring the fewest assumptions.
Genesis 1 does not make “common sense” in the context of the universe as we can plainly see it today, so I choose to look for truth revealed more abstractly there.
The rest of the “prehistoric” material, though, is easier for me to accept literally. To a quite large extent, much of it does in fact meet the commonsense test for me. In this post and hopefully the next, I’m going to walk you through that material, starting in Eden and ending in the world after Babel.
There is actually a lot of material here, and since I’m confident that there is a lot of misunderstanding in Christian traditions about the era, I’m going to cover only the things I don’t think you are likely to have been taught… or taught correctly!
In this post, we’ll walk through the next three chapters of Genesis, where I’ll point out some more interpretations that you may not have heard before, regarding creation day 7, the Garden of Eden, the Temptation, and Adam’s most prominent children.
I’m sure you’ve noticed that my writing tends to get a bit deep occasionally, and what follows is no exception.
The reason for that is because I present a lot of interpretations (even occasionally one of my own) that veer from the “strictly orthodox“. When I challenge church traditions that have no, or in my view insufficient, textual backing, then I think I have to provide some solid evidence. If some of it goes over your head, then at least I hope you’ll try to skim through it for the gist. Whether I’m right or wrong, I don’t want you to think I’m making things up!
Day 7
Genesis 2:1–3
This “seventh day of creation” is appropriately split off into Chapter 2 in modern translations of Genesis because it is fundamentally different from the other six days. While this may be a continuation of the dream series I postulated for Genesis 1, the “evening and morning” motif is conspicuously missing.
The Sabbath
No creation is done on this day. Instead, it is used to set a spiritual principle for the importance of rest and renewal. More importantly, it is also a celebration of Creation, in particular for the Creator Himself, Yahweh.
The suggestion that God needed a day to rest from His labors is of course a literary device, not a serious concern. God is a spirit (רוּחַ, ruach), physically encompassing and controlling the entire universe. He has no nutritional requirements, and evidently His activities expend no energy that would require replenishment.
He is, however, the ultimate source of order on earth and in the universe at large! Much of what follows is about God maintaining and, when necessary, reestablishing order in Creation as evil spreads on earth, and even in the celestial realm.
Calendars
The concept of weeks as a calendar-ordering system predates Moses. The earliest archaeological evidence for the grouping of solar days into weeks (usually, but not always, 7-day cycles) appears in the era of Nimrod, about 2300 BC. The practice of assigning ceremonial purpose to one or more days each week may go back almost as far.
The Hebrews were apparently first to sever the cycle of weeks from the monthly and annual cycles—meaning, for example, that a calendar week for most of the modern world is always exactly seven days, irrespective of how many days may constitute a month or a year.
The Host
One very important factor that’s usually missed in studies of these three short verses is the word “host.” Ignoring here the modern “host and hostess” concept, “host” is the Hebrew: צָבָא (tsaba) meaning a large number of something, an army, or war.
[2:1] Thus the heavens and the earth were finished, and all the host of them.
—Genesis 2:1 (ESV)
In modern English, we think of “host” in generic terms, for example, “a host of reasons.” ESV, NKJV and YLT, like KJV, have left further interpretation of the term, as it appears in verse 2:1, up to the reader, but many modern translations go further and assume that it is speaking of a large number of created “things”, like stars, planets, etc. Examples of such translations include:
- “Everything in them”, CJB, HCSB
- “All that filled them”, NCV
- “In all their vast array”, NIV
- “In all their multitude”, NRSV
- “All their inhabitants”, AMP
- “All their heavenly lights”, NASB
A Biblical lexicon or a concordance lists the various ways that a word has been translated, without passing judgement on how it should have been translated. I believe that the term “host” in Genesis 2:1 and other passages with a similar context is speaking not of inanimate or miscellaneous things, but specifically of the angelic armies that God created to manage the cosmos. Translators have mostly missed this connection because angelology is so poorly understood and under-appreciated by most theologians.
Note that God is often referred to in Scripture as Adonai Sabaoth, “The Lord of Hosts/Armies.” Angelic beings are not just an afterthought, pets, slaves, or “gofers” of any kind. They are important residents of the created universe, members of God’s heavenly family.
I believe that this verse sets the time of their creation: At or near the beginning of the 13+ billion-year life of the universe.
Of course, that also fits with the concept that the Host was created to do for the universe what humankind was to do for the inhabitable earth: To subdue it and maintain it.
The garden
Genesis 2:4–24
I discussed Genesis 2 and 3 in detail in Exploring the Garden of Eden. Briefly, I believe that they were real people living in a real Garden of Eden, and their temptation and failure were real events. Beyond that, as explained there I do have some issues with traditional interpretations:
Chapter 2 outline
- Gen 2:4 is a toledah, a genealogy marker, separating the previous text from what follows, which I believe is a separate creation story, not a retelling of any part of chapter 1. Gen 1:26 describes the creation of early man, before Adam and Eve were added to their number to perform a specific function.
- Gen 2:5–6 describes conditions, not over the entire earth, but just over the land (אֶרֶץ, eretz) that would become the holy Garden. Eden was too arid to support any “bush of the field” (wild vegetation) and it was not as yet inhabited, or under cultivation.
- In Gen 2:7, Adam was formed (יָצַר, yatsar) by God, not created ex nihilo (בָּרָא, bara’) as in Gen 1:26. “Dust of the ground” refers simply to the chemical elements occurring on earth, perhaps specifically in the soil of the Garden. The “breath of life” is something that I don’t believe can happen spontaneously through any “Biopoiesis” process, i.e., “a supposed origination of living organisms from lifeless matter” as assumed by all non-theistic evolutionary theories. Note: “Panspermia” theories (life seeded on earth from extraterrestrial sources) don’t solve the ultimate question: How did the first life arise? It has never been shown how non-life can become life, aside from creation.
- In Gen 2:8–9, God then (after forming Adam) planted (נָטַע, nata, not a creative act, though no doubt done with a supernatural boost) a garden (גַּן, gan, an enclosed area, normally in those days planted with trees) “eastward in Eden“. This garden was not Eden itself but was an area evidently on the eastern side of a region by that name.
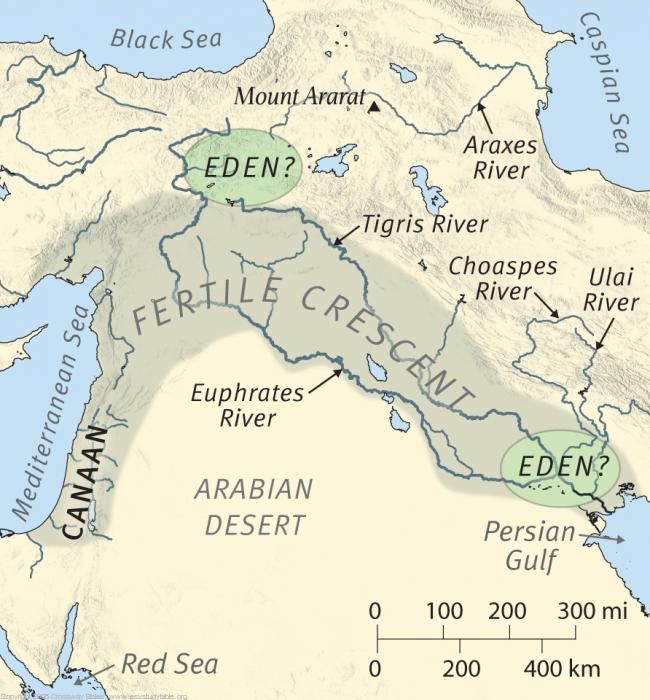
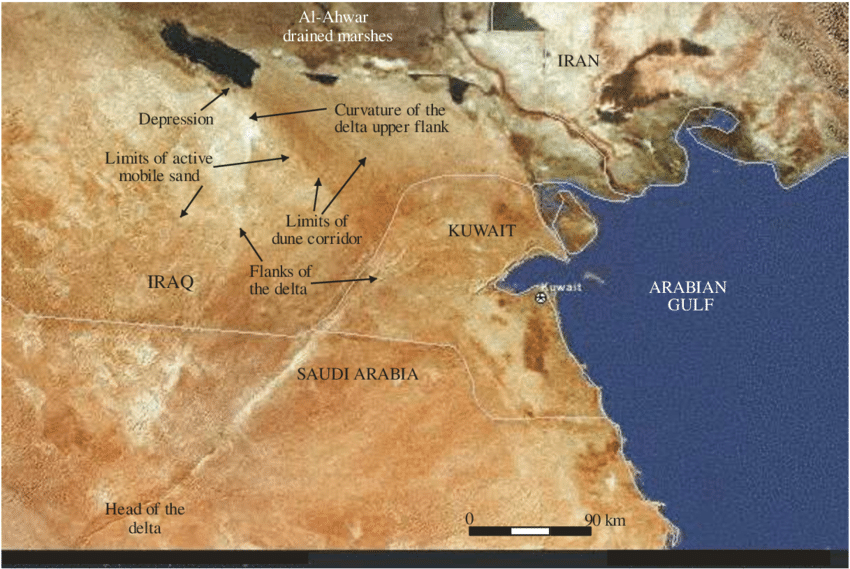
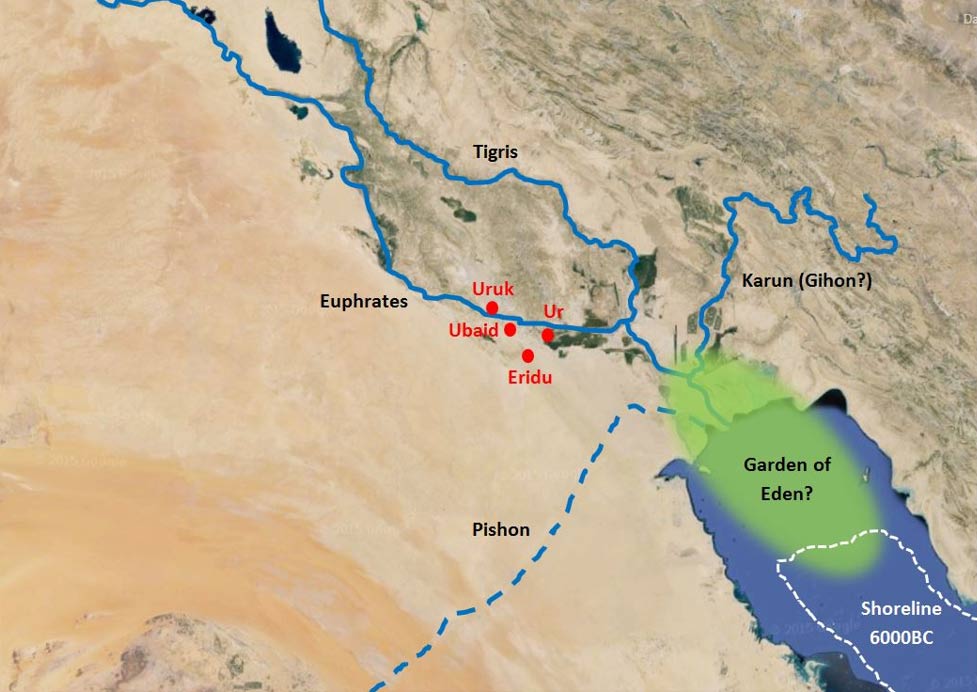
- In Gen 2:10–14, “A river flowed out of Eden to water the garden…”. The river flowed out of Eden and into the Garden. “There [presumably in Eden, upstream of the Garden!] it divided and became four…” Not simply “rivers” or “streams” as most translations state, but רֹאשׁ (ro’sh), meaning in this case “headwaters“, that is, the source waters that filled the river running into the Garden. In my Garden of Eden post, I explain why rivers that divide running downstream are unstable and quickly either recombine, divert into a single channel or dissipate altogether. I then use this information to firmly establish the location of the Garden in present-day southern Iraq—from information contained in the Biblical account.
- In Gen 2:15–17, there is no prohibition of eating from the Tree of Life. Gen 3:22 implies that it was in the Garden in order to give Adam and Eve a semblance of immortality, which further suggests that they were not created immortal to begin with. See Romans 5:12 and Death Before the Fall.
- In Gen 2:18–24, once God announced (surely to His Divine Council) that He intended to make a suitable helper for Adam, He first allowed the man to observe what that concept meant to other creatures. Animals had already been created (bara’, ex nihilo) outside the Garden. Rather than resume the creation (bara’) process discussed in Gen 1, He chose now to form (yatsar) new animals from the elemental “dust”, in the same way He had formed Adam. From the context, these were male/female pairs. Whether they were existing species or freshly designed for the Garden is unspecified. My own assumption is that Adam’s task was to become familiar with them to the extent that he gave them personal names, like Mickie and Minnie, for instance, rather than “male and female deer mouse” (Peromyscus maniculatus). Once Adam understood the picture, God made him an appropriate human companion.
The garden’s function
Over the years I’ve heard several suggestions that the Garden of Eden, in addition to being an idyllic home for Adam and his family, was actually a prototypical tabernacle for worship of Yahweh.
This is fodder for a future full article on its own, but for now I’ll just say that I agree! All of the necessary elements are in place, and the Garden as Temple/Tabernacle fits nicely with my knowledge of the way God typically does business. When you study the history of such facilities, you see that the Temple serves as a “home” for Yahweh in the midst of His people. We know that God is omnipresent in the universe, but as long as His people are obedient, He delights in maintaining an “interface” with them, as for example, His sh’kinah presence hovering over the Ark of the Covenant in the Holy of Holies.
In this verse, the picture is not one of God dwelling in heaven and periodically visiting in the Temple. It is one of God remaining in the Temple where He is accessible. For example, among the blessings of keeping His commandments, God promises:
[11] I will put my tabernacle among you, and I will not reject you, [12] but I will walk among you and be your God, and you will be my people.
—Leviticus 26:11–12 (CJB)
When King David offered to build a permanent Temple in Jerusalem, God replied:
[6] Since the day I brought the people of Isra’el out of Egypt until today, I never lived in a house; rather, I traveled in a tent and a tabernacle. [7] Everywhere I traveled with all the people of Isra’el, did I ever speak a word to any of the tribes of Isra’el, whom I ordered to shepherd my people Isra’el, asking, “Why haven’t you built me a cedar-wood house?”’
—2 Samuel 7:6–7 (CJB)
The concept of God “tabernacling” with His people is so important that, out of the seven feasts that Israel was ordered to observe every year in perpetuity, it is celebrated by the most joyous and anticipated feast of all. The Feast of Tabernacles is celebrated in Jerusalem and around the world beginning on Tishri 15 every year. In fact, it is such an important occasion that Tishri 15 of the Gregorian year 4 BC was the date that Yahweh chose for the Son to be born in Bethlehem (see The Jewish Feasts: Part 14, Tabernacles)!

Given the above, God’s activities in verse 8, below, are explained very well:
[8] They heard the voice of ADONAI, God, walking in the garden at the time of the evening breeze, so the man and his wife hid themselves from the presence of ADONAI, God, among the trees in the garden.
—Genesis 3:8 (CJB) emphasis mine
The temptation
Genesis 3
This is a vitally important passage of Scripture, and I am 100% convinced that the essential lesson—that the very real Satan tempted the very real Adam and Eve and brought about very real and horrendous curses that still afflict this planet—is absolutely true.
I would refer you to Exploring the Garden of Eden for a fairly comprehensive exposition of this chapter. I do, however, have a lot more to say here about one of the principal characters of the story:
The serpent
I have read somewhere that the serpent, prior to its curse, was a quadruped and the most beautiful of all the animals on earth. How could anyone know that? Obviously, the idea is pure fantasy!
As a matter of fact—don’t hang up on me here—by today’s literary standards the serpent story is a fable, along the lines of Rudyard Kipling’s famous tales like How the Camel Got its Hump, or How the Leopard Got its spots. But read on before you judge me too harshly…
In the ancient world of the fertile crescent, the genre of “fable” was a common and respected way of transmitting real history. What made a story a fable was not that it was necessarily fiction, but that it contained a moral lesson. In mid-2024 I wrote a short (believe it or not) article titled Religion vs. Mythology in which I quoted Egyptologist Bob Brier: “Mythology contains stories [set in the primordial past] that are not [necessarily] to be taken literally but answer basic questions about the nature of the universe.”
In other words, mythology usually contains at least some metaphorical historical content but always seeks to teach a useful lesson about reality. The question here becomes, “What part of the Serpent story, if any, is metaphorical? I’ll answer that with a brief analysis framed as a Q&A:
- First, was the serpent really Satan, as we’ve all been taught?
Absolutely! That point is clarified several times in Scripture, including:
[20:1] Then I saw an angel coming down from heaven, holding in his hand the key to the bottomless pit and a great chain. [2] And he seized the dragon, that ancient serpent, who is the devil and Satan, and bound him for a thousand years,
—Revelation 20:1 (ESV)
- Was Satan really a snake?
No, that’s the metaphor part. To unbelievers, everything supernatural in the Bible is by definition metaphorical. That is no reason for believers to dismiss the possibility that God used metaphor at times when the cultural context made metaphor the best way to dramatize a truth.
If you find slithering snakes to be creepy, well, so did the ancients. Not only are their appearance and habits unsettling and their nests often hidden and/or in the wilderness, which is where all matter of evil spirits were known to reside, but they are of course potentially very deadly.
Snakes were plentiful in the Ancient Near East (ANE), and they were of course the subject of much supernatural dread. Snake images were associated with a number of the pagan gods and were appropriated by pagan human rulers to demonstrate their association with those gods.
- If Satan wasn’t a snake, what was he?
Satan was a corrupt, high-ranking angelic being, a spirit with the ability to take on corporeal form, like a human or, in this case, a reptile. Specifically, he was a cherub:
[14] You were a keruv [cherub], protecting a large region;
I placed you on God’s holy mountain.
You walked back and forth
among stones of fire.
—Ezekiel 28:14 (CJB)
Cherubim and Seraphim (while not technically “angels”) are spirit beings created to guard God’s throne and other sacred objects. The terms “garden of God” and “mountain of God” refer to any location where Yahweh is “officially” in residence. The “stones of fire” are the spirits present: Yahweh, His guardians, and the “sons of God” on His “Divine Council.“
I won’t document those definitions here, except to point out that God didn’t “come down” to visit with Adam and Eve; He was coresident with them in Eden, along with His spirit retinue. Satan was present, as a matter of course. He violated the trust given him by God. The verses following the passage last quoted tell the consequences:
[15] You were perfect in your ways
from the day you were created,
until unrighteousness
was found in you.
[16] “‘When your commerce grew,
you became filled with violence;
and in this way you sinned.
Therefore I have thrown you out, defiled,
from the mountain of God;
I have destroyed you, protecting keruv,
from among the stones of fire.
[17] Your heart grew proud because of your beauty,
you corrupted your wisdom for the sake of your splendor.
But I have thrown you on the ground;
before kings I have made you a spectacle.
—Ezekiel 28:15–17 (CJB)
- Did Adam and Eve see a snake, or something else?
Yes… Okay, my guess is that they saw a snake, but whatever they saw or sensed, they recognized him as one of the resident cherubim. There is no mention of fear, or of surprise at a talking snake.
- If Satan wasn’t really a snake, then why did God curse snakes?
Good question! The answer is, He didn’t!
It sounds like He did, but remember that I’m billing this as “mythologized” history. Real history, told in the dramatized way that history was frequently taught in antiquity. Snakes weren’t beautiful quadrupeds before the fall, they were beautiful… snakes! God designed snakes to “crawl on [their] belly” because that is what best suited them for their ecological niche. As for “eating dust”, that isn’t a snake function, but I imagine it does happen from time to time, given their proximity to the ground. I’m confident that snakes are quite happy in their own niche! And many of them are still quite beautiful.
- But why would a Cherub be given a snake’s punishment?
What God actually cursed was the being that was impersonating a snake: Satan, a.k.a., the Serpent. The persona that Satan chose to adopt, or that Moses chose to assign to him, was that of a Serpent, and Satan’s curse was worded accordingly.
That curse is given in Genesis 3 and is explained in the Ezekiel passage quoted above and in Isaiah:
[11] Your pride has been brought down to Sh’ol
with the music of your lyres,
under you a mattress of maggots,
over you a blanket of worms.’
[12] “How did you come to fall from the heavens,
morning star, son of the dawn [Lucifer, son of the morning in KJV]?
How did you come to be cut to the ground,
conqueror of nations?
[13] You thought to yourself, ‘I will scale the heavens,
I will raise my throne above God’s stars.
I will sit on the Mount of Assembly
far away in the north.
[14] I will rise past the tops of the clouds,
I will make myself like the Most High.’
[15] “Instead you are brought down to Sh’ol,
to the uttermost depths of the pit.
—Isaiah 14:11–15 (CJB)
It takes some context to understand it:
[14] ADONAI, God, said to the serpent, “Because you have done this, you are cursed more than all livestock and wild animals. You will crawl on your belly and eat dust as long as you live.
—Genesis 3:14 (CJB)
- In Biblical imagery, the celestial “angels” are compared to stars in heaven. The highest ranking of these beings are called the “sons of God,” and are likened to the “morning stars“, stars that are bright enough to shine even as the sky lightens near sunup.
- Ezekiel says that “When your commerce grew, you became filled with violence”, and Isaiah calls him a “conqueror of nations.” “Growth of commerce” means increase in power and renown. Just like humans, spirit beings have free will and thus a propensity for pride, arrogance, and envy. I don’t know what, specifically, the prophets had in mind here, but evidently at some point in his 13-billion-year life, he became involved in battles involving either other angelic beings, or humans, or both.
- Genesis 3 marks the last straw for God. Satan’s lies to Eve and contradiction of God rose to open rebellion, which the Most High could no longer tolerate. [Note: this is the first of three angelic rebellions in Scripture; the other two will be covered in my next post.]
- Because of the context in which it was uttered, “You will crawl on your belly and eat dust as long as you live” does indeed sound like perhaps a quadruped is being cursed to lose its four legs and instead slither from place to place. But what are we left with if we remove the mysterious quadruped from the snake story?
In Ezekiel 28:17, we read “But I have thrown you on the ground” and in Isaiah 14:15, we have “Instead you are brought down to Sh’ol, to the uttermost depths of the pit.”
In Ezekiel, the Hebrew word translated ground is אֶרֶץ (eretz). Eretz can, in some instances, be translated country, earth, field, ground, nations, way, and a few more alternatives. In the NAS Exhaustive Concordance, the word is most commonly (1,581 times) translated as “land.” In such cases the application is almost always to holy land, usually to the Land of Israel (eretz Yisrael), but also to the Garden of Eden, Mt. Sinai, the Tabernacle and other places marked for worship of Yahweh.
Key here, though, is that eretz is often used, especially in ancient Hebrew extrabiblical writings, as a euphemism for Sh’ol, a.k.a., the underworld, the pit, or the place of the dead. This immediately brings Ezekiel 28:17 into alignment with Isaiah 14:15, where Sh’ol is mentioned explicitly.
I have no doubt whatsoever that this is the Serpent’s curse, stated pictorially in accordance with the fable genre.
Satan or satans
With Satan kicked out of heaven as early as the Garden of Eden, you may wonder how it is that he is apparently welcomed back to have cordial chit-chats with God over things like Job’s faith…
A lot of my material in this post comes from the books of the late Michael S. Heiser: The Unseen Realm, Demons, Angels, Reversing Herman, etc. Also, books and papers that he cites. Most of what he teaches strikes me as solid exegesis, and makes good, common sense. With respect to his angelology and demonology, and his Old Testament theology and ANE history, I’m pretty much fully onboard with him. But though I am a Trinitarian, his arguments in support of that doctrine seem weak to me, and I leave his train altogether when he talks about the Church now being “the true Israel.”
With respect to this particular section, I’m firmly onboard with him, but many scholars are not. This is perhaps a good place to remind you that, while I think my principal spiritual gift is theological discernment, you are free to disagree. Please remember that I don’t believe that inspired prophets still exist among men, and I have no illusions that my posts are “inspired.” Neither are Heiser’s books.
As with so many other “fringe” doctrines that we’ve grown up believing, the idea that the Serpent of the Garden, the “archenemy“, is the “satan” of Job is an assumption made long ago that can’t be proven from Scripture.
I’m way past caring about “orthodoxy”; my desire is to understand the Person and Word of God to the best of my ability. If I’m wrong, I’m wrong…
Heiser points out that the Hebrew noun, שָׂטָן (satan), occurs only a couple times in the Old Testament without a definite article. Every other occurrence is in the form הַשָּׂטָ֖ן (hasatan), meaning “the satan“, i.e., “the adversary“, or “the accuser.” This is probably not the same guy!
The grammatical rules for Hebrew match English in this respect: When prefixed by an article (“a”, “an”, or “the”), a noun is meant to be used as a common noun. “Satan” is a name for one particular being. “The satan” describes Satan and other beings, presumably of much lower rank than the Serpent.
As Heiser says, you can call him “Mike”, but it isn’t grammatically correct to address him as “the Mike.”
Considering the satan in Job:
[6] It happened one day that the sons of God came to serve ADONAI, and among them came the Adversary [the satan, Hebrew: hasatan]. [7] ADONAI asked the Adversary, “Where are you coming from?” The Adversary answered ADONAI, “From roaming through the earth, wandering here and there.” [8] ADONAI asked the Adversary, “Did you notice my servant Iyov [Job], that there’s no one like him on earth, a blameless and upright man who fears God and shuns evil?” [9] The Adversary answered ADONAI, “Is it for nothing that Iyov fears God? [10] You’ve put a protective hedge around him, his house and everything he has. You’ve prospered his work, and his livestock are spread out all over the land. [11] But if you reach out your hand and touch whatever he has, without doubt he’ll curse you to your face!” [12] ADONAI said to the Adversary, “Here! Everything he has is in your hands, except that you are not to lay a finger on his person.” Then the Adversary went out from the presence of ADONAI.
—Job 1:6–12 (CJB)
The occasion is a standard gathering of the Divine Council. The “sons of God” were created for the purpose of assisting God in the administration and governance of the vast universe. Their duties included advice and council, which was the function of this assembly. Does God need any of this help? I assume not (He’s God!), but they are His created family, and He values their fellowship and assistance. Just as we believe God values the fellowship and assistance of His earthly family—us!
Ranking below the sons of God in the Heavenly Host are a group of “satans”, whose function is to “roam through the earth, wandering here and there” (Job 1:7), keeping tabs and reporting back. Heiser compares them to a prosecutorial staff. Or, as I think of it, a “Heavenly OSHA.” In this passage, the satan is just doing his assigned task. He’s not behaving in an evil fashion at all, and there is no hint of rancor in the conversation.
If you think that is a fanciful interpretation of Job, consider the following Divine Council example from 1 Kings: This is the prophet Micaiah describing his vision of a meeting of the Council in which Yahweh has asked for advice on how best to entice the evil King Ahab into a hopeless battle:
[19] And Micaiah said, “Therefore hear the word of the LORD: I saw the LORD sitting on his throne, and all the host of heaven standing beside him on his right hand and on his left; [20] and the LORD said, ‘Who will entice Ahab, that he may go up and fall at Ramoth-gilead?’ And one said one thing, and another said another. [21] Then a spirit came forward and stood before the LORD, saying, ‘I will entice him.’ [22] And the LORD said to him, ‘By what means?’ And he said, ‘I will go out, and will be a lying spirit in the mouth of all his prophets.’ And he said, ‘You are to entice him, and you shall succeed; go out and do so.’ [23] Now therefore behold, the LORD has put a lying spirit in the mouth of all these your prophets; the LORD has declared disaster for you.”
—1 Kings 22:19–23 (ESV)
One of God’s spirit advisors has suggested a plan. Yahweh approves it, and Yahweh assures that it succeeds.
Don’t misunderstand… Satan, the Serpent, is real and malevolent, the Archfiend. This is Paul’s “roaring lion”, and the Dragon of Revelation.
Nevertheless… I’m saying that not all mentions translated “Satan” in the Old Testament are about Satan, the Serpent of the Garden. Most of them are random satans (small “s”), including the satan of Job. Jesus Himself was functioning as “a satan” (an adversary) when He cleansed the Temple.
The banishment
A few observations from verses 20–24:
- What Adam actually named his wife, in Hebrew, was חַוָּ֑ה (Chavah). I know, it’s impossibly idealistic, but if someone goes by José, it seems to me to be insulting to call him Joe. Unfortunately, the Hebrew “ch” sound is a very difficult guttural for English speakers to pronounce.
- I’ve seen many suggestions that the animal-skin garments that God made for Adam and Eve (sorry, Chavah!) were from animals sacrificed as a blood atonement. No. They got what God promised they would get for eating the forbidden fruit! But let’s examine the rationale for the view:
The verse most often quoted is:
[22] And almost all things are by the law purged with blood; and without shedding of blood is no remission.
—Hebrews 9:22 (KJV)
But this is a general statement about the use of blood in cleansing rituals of all kinds, and the immediate context is more about the purification of objects than of people. The Hebrews author is using an Old Testament scripture midrashically.
Midrashically refers to the method of interpreting biblical texts through midrash, which involves exploring deeper meanings, filling in narrative gaps, and providing ethical or theological insights. This approach allows for creative and expansive readings of scripture beyond the literal text. myjewishlearning.com
A midrash is by nature a secondary source that applies the primary source in ways that were not necessarily intended in that original. This is done frequently in the NT, particularly by Paul. It would be much more to the point here to quote the OT text being referenced by the Hebrews passage:
[11] For the life of a creature is in the blood, and I have given it to you on the altar to make atonement for yourselves; for it is the blood that makes atonement because of the life.
—Leviticus 17:11 (CJB)
The context here is that God, through Moses, is giving two reasons that consuming blood, or meat with the blood still in it, is prohibited to Jews under the Covenant: (1) because blood is necessary for life, it is considered to be virtually the same as that life; and (2) God has sanctified blood that is shed on the altar as a means of atonement.
But even that has to be analyzed further:
- Some primitive forms of animal life do not in fact, require blood for life, which doesn’t negate the point of the prohibition.
- Not all animal blood is efficacious for atonement, only the blood of ritually clean animals. Again, the prohibition stands.
- Every sacrifice, to be effective, must be done in accordance with the rules set down in the Covenant.
- Though sacrificial offerings were made as early as Cain and Abel, we know of no specific cultus yet available to govern them, nor of any specific rationale for doing them.
I contend that it is a misappropriation to assume from either passage that Yahweh has made a “blood sacrifice” on behalf of Adam and Eve. Animal skins are more durable and provide better insulation and padding than plant leaves. It’s enough for me to know that God was compassionate with respect to the physical and emotional needs of the freshly cursed humans.
- “Behold, the man…” הָֽאָדָם֙ (haadam). The same interpretive principal applies here as for Satan/hasatan: where the article is absent, a proper noun is intended; where it is present, expect a common noun. Adam (ah DAHM) is a name; haadam (hah ah DAHM) is a noun meaning “man”, “mankind”, or “human.” The latter is in view in verse 22.
- “…eat, and live for ever.” See above for the implication of the Tree of Life in the Garden.
- “…to till the ground from whence he was taken.” This is a bit ambiguous on its own and might give you pause. “The ground” is הָ֣אֲדָמָ֔ה (haadama). “Adam” comes from a Hebrew root meaning “red.” As does the related word adamah, meaning “earth” but referring not to the planet, but rather to the ground, especially (over 200 times in the Old Testament) to tilled land, productive soil, or Israel’s productive land in particular. The “ground” here refers not to the acreage within Eden, but rather more specifically to the “dust” from which he was formed.
- “…the east of the garden…”. Given the presumed nature of the Garden as a tabernacle, it’s no surprise that its access was on the east side. The same is true of all correctly built temples and synagogues. Prayer is directed towards Jerusalem’s Temple Mount, wherever you might be, but access to the “holy space” is always from the east, where the sun rises.
- “Cherubims” I’ve been quoting KJV in this list, and this word is grammatically incorrect, at least in this century. The Hebrew is הַכְּרֻבִ֗ים (hakerubim). “The cherubim” is plural without a trailing “s.” The singular of “cherubim” is “cherub“, which is an Anglicized transliteration of the Hebrew “kerub.” Cherubim, along with Seraphim, are heavenly “throne guardians.” Satan is a cherub. You probably picture just one cherub guarding the gate with a big sword in his fist, but there is a team of cherubim on hand here.
- “…a flaming sword…” I don’t know if this is a literal sword or some other device, and whether it is handheld, mechanized, or animated. Evidently there is only one, so if handheld, only one of the cherubim would be armed with one.
- What finally happened to Eden? My guess is that it was probably guarded until either it was finally destroyed, or until the Tree of Life was moved somewhere else. If it (the Garden) didn’t survive the centuries, it may have been swept away by the receding waters of the Great Flood.
Adam’s children
Genesis 4
Cain and Abel
Why was Cain’s veggie offering unacceptable? Maybe it included cauliflower or beets… That would do it for me!
Many will tell you that Cain’s offering was refused because it was not a blood sacrifice. Maybe, but I seriously doubt that interpretation. The Mosaic Covenant was still well over a thousand years in the future, so there was no standardized command for offerings that we know about. Abraham was over a thousand years in the future, too, so it wasn’t a Jewish thing.
(He did finally make a blood sacrifice, by the way… his brother!… that was refused, too.)
It has been suggested that God gave Adam a sneak preview of what offerings He was going to require in the future. Maybe.
In any case, they both made offerings from their own “sweat of the brow”, which would seem to be a good thing. With no information to the contrary, I would have to think that it had something to do with their respective motivations, or maybe he stole the veggies from Eve.
Other passages shed additional light:
[4] By faith Abel offered to God a more acceptable sacrifice than Cain, through which he was commended as righteous, God commending him by accepting his gifts. And through his faith, though he died, he still speaks.
—Hebrews 11:4 (ESV)
[24] and to Jesus, the mediator of a new covenant, and to the sprinkled blood that speaks a better word than the blood of Abel.
—Hebrews 12:24 (ESV)
[12] We should not be like Cain, who was of the evil one and murdered his brother. And why did he murder him? Because his own deeds were evil and his brother’s righteous.
—1 John 3:12 (ESV)
Aha! That last one is the answer. Cain’s rejection was not because of the form of his offering at all. Any offering he brought would have been rejected because God knew his heart!
Moving on, what was “the mark of Cain?” Don’t know, can’t know, so don’t care.
Where is the Land of Nod, to which Cain fled? The Bible says, “east of Eden,” which makes me think maybe Elam, or farther east than that. “Nod” is from the Hebrew נוּד (nuwd, pronounced “nude”), meaning to move to and fro, wander, flutter, or show grief.
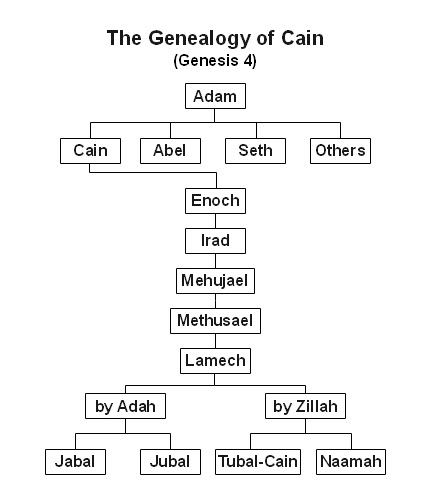
Cain’s descendants
Genesis 4:17–24
As I explained above, I regard Genesis 2:4 as, in essence, a toledah (singular), or genealogical “spacer” to separate the various historical threads that Moses wrote about in the book.
Technically, the toledoth (plural) are genealogies, the “begats” of KJV. The beginning of Gen 2:4 is translated by KJV and ESV as “These are the generations of the heavens and the earth…”, where “generations” is in fact the Hebrew תוֹלְד֧וֹת (toledoth). Other popular translations render it as, for example, “Here is the history…” (CJB) or “This is the account…” (NAS), which are paraphrases and not necessarily incorrect. But presence of the Hebrew term makes it officially a toledah and that strengthens my opinion that the forming of Adam and Eve is a different event than the creation of mankind in general.
Gen 4:17–22 is a genealogy of Cain, and it separates Cain’s part of the history from Seth’s, so technically the passage is a toledah, but because that term doesn’t appear in the text, it isn’t generally included in lists of the toledoth. The reason may be that if you remove verses 23 and 24, the entire passage, Gen 4:17–5:32 is a single long toledah. Alternatively, 4:17–22, are also about Cain’s extended family, so it could perhaps be included as part of the toledah.
My first reaction to verses 23 and 24 was to think, “well, they don’t conform to the way small bits of biographical information are inserted into some genealogies (see Genesis 10, which is itself one long toledah), but that must be what they are”, but looking at it today, it dawns on me that they seem out of place here, but they would fit perfectly in Chapter 6, which I will cover in a sequel to this post, under the heading “Corruption.” If this snippet wasn’t misplaced by scribal error, then it is simply an issue of author’s choice. Not a big deal.
I have just one more observation about Cain, until the next post.
Everyone wants to know… Where did Cain find a wife? Young Earth Creationists would say he took a sister with him to Nod. Possible, but creepy, so I’d rather it not be so. In any case, to me it is more likely that she was a member of one of the pre-Adamic races descended from the humans created in Genesis 1:26.
Seth
Genesis 4:25–26
[25] And Adam knew his wife again, and she bore a son and called his name Seth, for she said, “God has appointed for me another offspring instead of Abel, for Cain killed him.”
—Genesis 4:25–26 (ESV)
Seth’s name in Hebrew is שֵׁ֑ת (Sheth, pronounced “shayth”). It is a play on the similar word שִׁית (shiyth, pronounced “sheeth”), a verb meaning, “to place.” Both of these words appear in verse 25. The latter is translated as “appointed” in the KJV and ESV, and that is close enough. Interestingly, it is the same word as used in Genesis 3:15, “I will place (shiyth) enmity between [Eve’s and the Serpent’s seeds].”
Verse 26 mentions Seth’s son, Enosh, a name which I’ll point out in the next post is a mildly derogatory word denoting a man but connoting one who is not quite top-drawer. Perhaps he is mortal or not a gibbor, or hero.
Not much is reported about Enosh, but the verse states that during his lifetime, “…people began to call on the name of Yahweh.” All that this means to me is that it wasn’t until the time of Adam’s grandchildren that humans from the family of the Garden began to appreciate the power of God and to seek His favor.
Many scholars, though, quote this verse in order to advance the theory that the “sons of God” in Genesis 6 are humans from the “godly lineage of Seth,” which I consider to be a ridiculous interpretation. I will address that issue in that next post.
Coming next
What follows is an update written on January 21, a month and a half after first publishing this article.
Usually, I don’t pick my next topic until I’ve had a week or two to recover from the last. This time, I had already decided to cover the remainder of what I’ve called my survey of Moses’ prehistoric account of the days before Abraham.
Instead, I’ve decided to break that material into at least two articles because of the complexity of the study.
I’ll start with a post covering the period following the life of Seth, up to the Flood. The centerpiece of that study will be a discussion of the period of intense corruption, both in heaven and on earth. The core of that material is from the first five verses of Genesis 6. Everyone is familiar with the words of that passage, but because it is so bizarre, it is rarely taught, and from the days of Augustine of Hippo (who was the first patristic father to butcher it), understanding has been almost non-existent.
Yet, despite the intervening flood, its effects reverberate through both the Old and New Testament, to the last verses of Revelation.
Then, in hopefully just one post:
- I’ll gloss through the Flood story, because I have already covered that thoroughly in several posts.
- Then I’ll spend some time with Babel and the scattering.
- And finally, I will possibly surprise you at my commentary on Nimrod.
The time span of this series of articles covers all three major angelic rebellions, and the three combined (not just the Temptation) account for the horrible state of the current world and the need for Jesus’ hopefully imminent return.