Posted on:
Modified on:
- The language of Image and Likeness
- The nature and attributes of God
- Defining “God’s Image and Likeness”
So, what does that term, image, even mean? Here’s a paraphrase of Merriam-Webster® as it applies to an image of a person (or a being like a god or angel):
- A reproduction or imitation of the form of a person; especially, an imitation in solid form (a statue).
- A visual representation of someone captured by an optical or photographic device of some sort.
- A person that is an exact likeness or close duplicate of someone else.
- An incarnation or apparition of someone.
- A mental picture, impression, or conception of a person held in common by members of a group.
- A vivid or graphic representation or description of a person.
- A popular conception or caricature of a person.
Well, that’s a start, but we have to be careful when we impose English translations on another language, especially a language as spoken 2,000 years ago and before.
The language of Image and Likeness
The Bible claims that man was created in the image and likeness of God. We are all aware of that, but there is wide disagreement about what it means. Here are the relevant Scriptures:
26 Then God said, “Let us make man in our image, after our likeness. And let them have dominion over the fish of the sea and over the birds of the heavens and over the livestock and over all the earth and over every creeping thing that creeps on the earth.”
27 So God created man in his own image,
in the image of God he created him;
male and female he created them.
— Genesis 1:26-27 (ESV)
1 This is the book of the generations of Adam. When God created man, he made him in the likeness of God. 2 Male and female he created them, and he blessed them and named them Man when they were created.
— Genesis 5:1-2 (ESV)
6 Whoever sheds the blood of man,
by man shall his blood be shed,
for God made man in his own image.
— Genesis 9:6 (ESV)
Image
I found 15 Hebrew words in the Old Testament (OT), categorized by 15 different Strong’s numbers, that are sometimes or always translated as “image.” Almost all of those refer specifically to idols, either in general or by category, or sometimes descriptively, as “abomination.”
However, I will concentrate here on the one word for “image” that appears in the above verses:
צֶלֶם, tselem (H6454), per Strong’s Exhaustive Concordance, “From an unused root meaning to shade; a phantom, i.e. (figuratively) illusion, resemblance; hence, a representative figure, especially an idol — image, vain show.”
Elsewhere, this particular word is used:
- In Genesis 5:3, to describe Seth as a son of Adam.
- In Numbers, 1 Samuel, 2 Kings, Ezekiel, and Amos, in reference to various types of idol.
- In Psalms, to refer to a man’s shadow or his phantom.
Likeness
“Likeness” is a translation of the Hebrew,
דְּמוּת, dmuwth, per Strong’s Lexicon, “Likeness, resemblance, similitude.” Note that “likeness” and “resemblance” refer to similarities in appearance or other traits. “Similitude” includes the above meanings, but also more general comparisons, like similes, analogies, caricatures, patterns, correspondences between abstractions, or modern concepts like photographs.
In Genesis 1:26, it refers to Seth’s likeness to Adam, but elsewhere in the OT it usually refers to prophetic visions, as in Ezekiel 8:2, “Then I looked, and behold, a form that had the appearance of a man.”
The nature and attributes of God
When reading in the Bible that God created humankind in His image, there is an almost overwhelming tendency to assume something from the list of 7 definitions for “image” at the top of this article. But what all seven of those definitions have in common is that they all pertain to the physical substance of a person or being. But does God have any physical features that can be visualized, i.e., “imaged?”
Does God have a body?
When many unsophisticated people, Christian or not, visualize God, they probably see something like this digital artwork:

It’s true that the Bible does sometimes speak of God in human terms, describing Him as having eyes, ears, mouth, hands and arms. But almost all theologians recognize these as anthropomorphisms, which are common in the literature of Israel and the Ancient Near East in general.
According to literarydevices.net anthropomorphism is “a technique in which a writer ascribes human traits, ambitions, emotions, or entire behaviors to animals, non-human beings, natural phenomena, or objects.”

The Bible also describes God as having wings and feathers:
He will cover you with His feathers,
and under His wings you will find refuge.
His faithfulness is body armor and shield.
— Psalm 91:4 (TLV)
As a young man, one of my most cherished pastors fervently believed that God has a humanoid body. He took the position on all things Biblical that, “The Bible says it, I believe it, and it’s so!” Well, in general that’s a good approach, but the Psalms are poetry and songs, and that genre of Scripture in particular (along with prophecy) contains a lot of figurative language. No, God is not a bird. Or even an angel.
God as a spirit
The overwhelming evidence of Scripture is that God is a spirit.
Be careful here. When we read about “the spirit of God” or the “Holy Spirit“, that is a different subject, which you can read about in Monotheism and the Trinity. I won’t get into that here.
One verse makes the spiritual essence of God more or less explicit:
23 But the hour is coming, and is now here, when the true worshipers will worship the Father in spirit and truth, for the Father is seeking such people to worship him. 24 God is spirit, and those who worship him must worship in spirit and truth.”
— John 4:23-24 (ESV)
Once again, caution is necessary. Nobody with a theological background ever said the Bible is crystal clear from cover to cover. The subject of this verse is, “those who worship him must worship in spirit and truth.” The independent clause, “God is spirit”, is a little ambiguous without further definition.
Other verses imply the same thing by pointing out that He is immortal and invisible, both of which are not characteristics of corporeal beings. For example:
To the King of the ages, immortal, invisible, the only God, be honor and glory forever and ever. Amen.
— 1 Timothy 1:17 (ESV)
15 He [Jesus] is the image of the invisible God, the firstborn of all creation.
— Colossians 1:15 (ESV)
The contrast drawn in the poetic doublet that starts Isaiah 31:3 suggests the same:
Now Egyptians are men and not God,
and their horses are flesh, not spirit.
— Isaiah 31:3a (TLV)
But above all, to my mind, God’s omnipresence and eternality necessitate His incorporeal nature. You can’t span all of the universe and all of time if you are encumbered by a physical body. Please read about this in detail in another previous post, Implications of God’s Omnipresence and Eternity in Space-Time.
God’s attributes
Theologians recognize a number of characteristics, or attributes, of God. Some of these, called the noncommunicable attributes of God, are characteristics of God and God alone. No other creature in the universe, including mankind or the Heavenly Host, can possess these attributes. We will never be omniscient or omnipotent, for example. Even our eternal life is not quite the same. God is “from everlasting to everlasting.” The best we can be is “from now to everlasting.” And even that is not ours by default; it is ours at God’s direction and at His pleasure.
By contrast, God’s so-called communicable attributes are shared to a lesser degree with angels, humans, and to a very small degree, animals. These attributes include:
- Sentience
- Consciousness
- Intelligence
- Ability to communicate
- Rationality
- Curiosity
- Emotionality
- Willfulness
- Conscience
- Religiosity
Defining “God’s Image and Likeness”
The Bible doesn’t explicitly state, in terms that are clear to the modern world, what it means to be “created in God’s image and likeness“, which is why there are so many opinions on the subject. We’ll examine some of these opinions, simplifying somewhat by treating image and likeness as nearly synonymous.
Attributes as image
Most proposals for understanding how mankind is an image of God hold that man is somehow a copy, though necessarily inferior, of some aspect of God Himself. Stated another way, that mankind has inherited from God, via creation, some arbitrary set of His attributes.
But if that is the case, we have to consider what particular aspect or aspects of God we could possibly possess that might in any way correspond to any part of Him.
Which of our human attributes, in other words, clearly mark us as an image Almighty God?
Physical attributes
I’ve already expressed the view that God has no physical body. That seems obvious to me, but it isn’t to everyone, and possibly not to anyone at all in the ancient world. Let’s examine here,
Why humans are or have been presumed by some to “look like God”
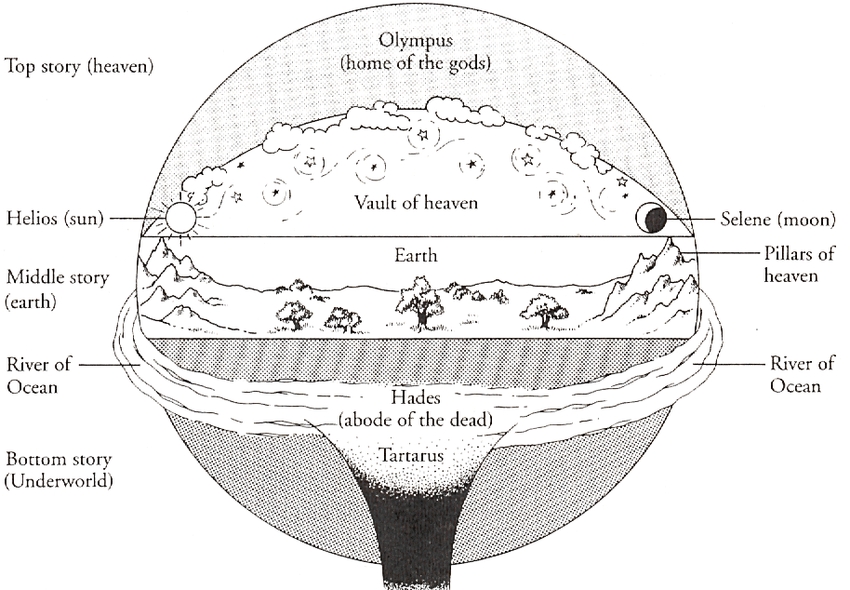
Because of common origins in the pagan culture of Babel, Biblical Israel and the surrounding nations shared many customs and conceptions. Their understanding of the nature of the universe is one example.

Another commonality you will see in pagan literature is that almost all peoples visualized the gods as having humanoid bodies, with perhaps animalistic features thrown onto some. I suggest that there is good reason for this:
8 And they heard the sound of the LORD God walking in the garden in the cool of the day, and the man and his wife hid themselves from the presence of the LORD God among the trees of the garden. 9 But the LORD God called to the man and said to him, “Where are you?” 10 And he said, “I heard the sound of you in the garden, and I was afraid, because I was naked, and I hid myself.”
— Genesis 3:8-10 (ESV)
The wording of this passage implies that the LORD God was walking in the garden in some tangible form, perhaps rustling leaves, disturbing stones and breaking twigs in passing. The fact that they recognized the sound indicates that He had probably done so in the past. In other Biblical theophanies, the form was apparently always humanoid, so as to soothe the fears of those He confronted. Angels who materialized in front of humans at God’s behest also did so in human form.
I would suggest (you’ll need to read on for an explanation of this startling idea) that the pagan gods (bad angels) on occasion did the same, often with some sort of “enhancement” to their form for the purpose of conveying the image, fierce, soothing, or whatever else that they wished for their people to see.
Bible readers often form the impression that the pagan peoples of the ANE (Ancient Near East) worshipped lifeless idols, and in fact that was a charge frequently leveled by the prophets to insult the worshippers. The fact is, though, that the idols were constructed as a “housing”, or focal point, for an invisible God or goddess who inhabited it. Who were those “gods”, and were they real?
According to the following passage, when God scattered the nations from Babel and “confounded their languages,” He assigned angelic overseers to each nation that resulted. Perhaps these particular angels were already corrupt, but if not, they eventually became corrupt and claimed to be gods.
8 When the Most High divided the nations, when he separated the sons of Adam, he set the bounds of the nations according to the number of the angels of God.
9 And his people Jacob became the portion of the Lord, Israel was the line of his inheritance.
—Deuteronomy 32:8–9 LXX-B (emphasis mine)
Ur, from which Abraham emerged, was probably inhabited by descendants of Shem’s son, Arphaxad. Verse 9, above, refers to the time when God, Himself, selected Abram/Abraham from the Ur2 culture and claimed His own portion, the family of Abraham’s grandson, Jacob.
For confirmation of this theory, read Daniel 10, where an angel sent to aid Daniel stated that he was delayed because “the prince of the kingdom of Persia” resisted him for 21 days until the angel Michael came to his rescue. Also, consider:
For we do not wrestle against flesh and blood, but against the rulers, against the authorities, against the cosmic powers over this present darkness, against the spiritual forces of evil in the heavenly places.
— Ephesians 6:12 (ESV)
Since God is clearly, in my view, a disembodied spirit, it is just as clear to me that we can’t look to His physical attributes to understand how we are His image.
He did not create us to look like Him!
Intellectual attributes
The communicable attributes of God are listed above, in part. I think of them primarily as intellectual attributes, because all of them involve mental capacity on some level. All originate in the brain.
Many folks think that we are God’s intellectual image and likeness. The following quotation, plus an evening spent reading through Job, should put that idea to rest!
8 “For my thoughts are not your thoughts,
and my ways are not your ways,” says ADONAI.
9 “As high as the sky is above the earth
are my ways higher than your ways,
and my thoughts than your thoughts.
— Isaiah 55:8-9 (CJB)
But in case it doesn’t, consider that virtually all animals think, on some level. Some species have less intelligence than others, but that doesn’t mean they have no intelligence at all. Yet, animals are nowhere said to be created in God’s image.
Furthermore, God’s image is a property imparted to all humans at creation. The corollary is that any child of a human that doesn’t possess all, or is missing even some, of the characteristics of God’s image, whatever it is, is not in fact human. If the intellectual attributes are what define God’s image, then unborn human babies, some of the disabled, or the comatose, would be excluded. On the flip side, my cat possesses all of those characteristics to some small degree. She thinks she’s human, but most of you would disagree with her self-assessment.
Family resemblance
Another view is that we are God’s image in the sense that a son is his father’s image. This view comes from,
1 This is the book of the generations of Adam. When God created man, he made him in the likeness of God.
…
3 When Adam had lived 130 years, he fathered a son in his own likeness, after his image, and named him Seth.
— Genesis 5:1, 3 (ESV)
While this doesn’t constitute proof, I first want to point out that while verse 3 uses the term “image” (tselem), verse 1 does not. The term “likeness” (dmuwth) is used in both verses and precedes “image” in verse 3. Recall that both terms can be used metaphorically, but that is much more frequently the case with “likeness” than with “image.”
I would suggest that the reason this argument from the wording is pertinent is the following:
The “family resemblance” argument for image is invoked, at least where I have heard it, because elsewhere in Scripture, redeemed humans are called “Sons of God” (Mt 5:9; Lk 20:36; Rom 8:14,19; Gal 3:26), just as the Heavenly Host (“angels”, aggelos in the NT) are called “Sons of God” throughout the Bible. But that is a statement of our standing before God, and our heavenly inheritance—not a claim that we are literally, genetically, sons!
The “likeness” here is a general similitude, an analogy of sorts. The father/son relationship is not in itself what constitutes the image of God. Yet the child does image the parent in many attributes, because of genetics.
Body/Spirit
Some see the image of God in the fact that we have a spirit like His. This is a confusing argument. It can be viewed in two ways:
First, if it is talking about the Holy Spirit, then that is no comparison at all. Yes, we have a spirit, but in no sense is it a separate entity. It is part of us, and inseparable from our body until death. The Holy Spirit on the other hand is an individual intellect, part of the Trinity, but with its own existence in some fashion not clear to mere humans.
On the other hand, if the argument is that we as humans have a spirit of our own, just like God does, then that is a fallacy because we have a spirit where God is a spirit. We could turn that around and say that we are a spirit with a body, where God is a spirit without a body.
Yet somatically (if that tangible terminology can be used intangibly), our spirit can be viewed (another misnomer) as similar in some ways to God Himself. That is a very rough similarity, though. The spirits of a human will always be bounded in space and limited to the current time in its “inertial frame of reference” (this is physics, don’t worry about it—just think of your current time as “now”), whereas God is infinite in scope and knows no boundaries in either space or time.
Trinity vs body/soul/spirit
This is a very popular choice with many, who argue that we are created in God’s image and likeness in that we, too, are a trinity—of body, soul and spirit! It boggles my mind that proponents of this view are often so dogmatic about it.
The only similitude between those two things is that they both can be said to be three-in-ones. But so is my house, which is two stories plus a basement.
I’ve already written about this comparison. Recently. It is one section of my post titled Monotheism and the Trinity, where I argue that a “trichotomous” human is not even a good analogy for the Holy Trinity. Because of its importance in this discussion, I repeat most of that section here:
Human as image
Another very common analogy that many Christians cherish is that of mankind as a “triune body/soul/spirit.”
This one is convincing to many because they see that arrangement as precisely what constitutes “the image of God.” I disagree for several reasons:
- A body/soul/spirit analogy assumes that we are God’s image ontologically. Ontology is the study of the nature and essential properties of something that exists.
But physically, we bear no resemblance to God whatsoever.
Intellectually, it may appear that we are similar (though inferior) to God, but I would argue that God, being unencumbered by a flesh and blood brain or even a computer chip, is intellectually more alien than anything we could possibly imagine. He is intimately connected to every facet of His creation in ways that are completely incomprehensible to us. That we know and understand an infinitesimal portion of what He does is only because He gave us the ability to observe and learn, using our vastly inferior senses.
- Furthermore, the body/soul/spirit analogy breaks down for me because I don’t think there is Scriptural support for this traditional trichotomous view of human ontology.
Yes, trichotomy (“division into three parts”) is suggested by:
1 Thessalonians 5:23 (ESV) emphasis mine
[23] Now may the God of peace himself sanctify you completely, and may your whole spirit and soul and body be kept blameless at the coming of our Lord Jesus Christ.
I don’t think there are any other passages that clearly list all three of these elements (and no others) in one place. There are many references that, taken alone, would support a dichotomous view (body/spirit), and even one that supports a tetrachotom0us view (heart/soul/mind/strength (where strength = body):
Mark 12:30 (KJV)
[30] And thou shalt love the Lord thy God with all thy heart, and with all thy soul, and with all thy mind, and with all thy strength: this is the first commandment.
In view of modern understanding that thoughts, emotions, behaviors, feelings, memory, and so much more are all housed in the brain, it makes most sense to me to believe that man is a soul, composed of a physical part that is fairly well understood and a spiritual part that is beyond our understanding.
Genesis 2:7 (KJV) additions mine
[7] And the LORD God formed man [the body] of the dust of the ground, and breathed into his nostrils the breath of life [spirit]; and man became a living soul.
- As an analogy for understanding the Trinity, I don’t think the body/soul/spirit view comes close, because the components that make up a human aren’t in any sense at all separate personalities. The body can of course “tell” the “spirit,” “I’m hungry” by growling its stomach, but where is the exchange of conscious intelligence in that?
Image as function
Personally, I agree with theologians like Michael S. Heiser and John H. Walton, who understand God’s image to be functional rather than ontological. We were created to function as His representatives, administrators of Earth.
Analysis of Genesis 1:26–28
We were created as human beings in order to represent Him on earth, for purposes set out in:
26 Then God said, “Let us make man [as] our image [agent; representative], after our likeness. And [as such] let them have dominion over the fish of the sea and over the birds of the heavens and over the livestock and over all the earth and over every creeping thing that creeps on the earth.”
27 So God created man [as] his own image,
[As] the image of God he created him;
male and female he created them.
[28] And God blessed them. And God said to them, “Be fruitful and multiply and fill the earth and subdue it, and have dominion over the fish of the sea and over the birds of the heavens and over every living thing that moves on the earth.”
— Genesis 1:26–28 (ESV) paraphrasing mine; see below for “as” in place of “in”
Genesis 1 was most likely, in my view, delivered to Moses as a prophetic (preterist) vision.
Verse 26 is written as prose and when shown as I have paraphrased it above, tells us what we are (26a) and what our function as “Imagers”, representatives, or administrators, is to be (26b). It is a stewardship over animal life on Earth.
In contrast, verse 27 is written as poetry. In the manner of most Hebrew poetry, the first two lines are a couplet, with the second line restating and thus amplifying the first. The added third line obviously isn’t telling us that our “image-ness” is in our being male and female—that surely in no way is a “likeness of God.” Rather, it seems to me, it is emphasizing something about the way we are created that enables us to accomplish our function as Imagers.
Verse 27 is a return to prose, that then tells us something more about our function as imagers: In order to take dominion over the living things of earth, we must use that male/female relationship to populate the planet with more of our kind.
Evidence from the Hebrew
When one looks up a Strong’s number for a Hebrew or Greek meaning, the entry found is not usually for the exact word found in the text. What is given is the “lemma”, or “uninflected” form of the word. The word found in the text itself is comprised of the lemma, modified by various prefixes and/or suffixes that define its actual intended usage in that particular location.
In Genesis 1:26–27, “image” is Strong’s H6754. The “H” stands for “Hebrew”, in case the same number, 6754 is also used for a Greek word in the NT. That entry in the Lexicon, whether Strong’s or another one that uses Strong’s numbers, shows meanings for the lemma, צֶלֶם, tselem (H6454), which I gave above.
But in the verse itself, the actual Hebrew is בְּצַלְמֵ֖נוּ, bə·ṣal·mê·nū represents the entire translated prepositional phrase, “in our image.” The prefix (Hebrew, including individual words, is written right to left, so a prefix is on the right side of the word) is בְּ, pronounced “bə.”
According to Hebrew and ANE scholar Heiser:
The preposition “in” should be understood as meaning “as” or “in the capacity of.” Humanity was created “as” the image of God. The concept can be conveyed if we think of “image” as a verb: Humans
are created as God’s imagers—they function in the capacity of God’s representatives. The image of God is not a quality within human beings; it is what humans are. Clines summarizes: “What makes man the image of God is not that corporeal man stands as an analogy of a corporeal God; for the image does not primarily mean similarity, but the representation of the one who is imaged in a place where he is not.… According to Gen 1:26ff, man is set on earth in order to be the representative there of the absent God who is nevertheless present by His image (Clines, ‘The Image of God in Man’)”
—Michael S. Heiser, The Lexham Bible Dictionary, “IMAGE OF GOD”
By this definition, which I find compelling, every Human is created to be an imager (representative) of God and the Eternal Realm on earth and eventually beyond, and that is not dependent on his or her stage of development, race, health, financial resources, location, or any other circumstance.
The commission
The first commission God gave to his Imagers was:
And God blessed them. And God said to them, “Be fruitful and multiply and fill the earth and subdue it, and have dominion over the fish of the sea and over the birds of the heavens and over every living thing that moves on the earth.”
— Genesis 1:28 (ESV)
He repeated this commission to Noah, on debarkation from the Ark:
And you, be fruitful and multiply, increase greatly on the earth and multiply in it.”
— Genesis 9:7 (ESV)
Again, to Jacob:
11 And God said to him [Jacob], “I am God Almighty: be fruitful and multiply. A nation and a company of nations shall come from you, and kings shall come from your own body.
— Genesis 35:11 (ESV)
Jeremiah predicted its eventual accomplishment:
3 Then I will gather the remnant of my flock out of all the countries where I have driven them, and I will bring them back to their fold, and they shall be fruitful and multiply.
— Jeremiah 23:3 (ESV)
And yet again: The “Great Commission.”
Another functional Model
I have been convinced for some time that our Image-hood is unlikely to be attribute-based. If God created us to resemble Him in any way, I can’t see it. Humans fall too short, in all ways that I can think of and in all ways I’ve heard suggested. We are commanded to try and be “Christlike”, but even that is a goal that I think nobody has ever achieved. Jesus is one of a kind!
Up until I undertook this project, I was considering another functional model: that perhaps we were created to be an analog of the pagan stone, wood or clay idols, a visible, external housing for God within.
On reflection, that seems to me now to be a very bad idea.
An idol supposedly concentrates attention on the location where “god” can be approached. The closest the One True God has come to that is designating one, and only one, Temple for that purpose. Inside the Temple, attention was in times past further drawn to the Holy of Holies, and within that to the Ark of the Covenant. But never was God said to inhabit the Ark. Instead, He was standing above it, using it as a “footstool.” With no question of God inhabiting the Ark, it could never become an idol.
The golden cherubim flanking the Ark were never going to be worshipped. Cherubim and Seraphim are angelic orders created for the express purpose of symbolic guarding of God’s throne. Occasionally their guardian roles are more than symbolic. Recall that cherubim (that’s a plural noun, so there was no doubt more than one) were stationed to guard the Garden after the Fall.