Posted on:
Modified on:
- The Flood
- After the Flood
- Return to Shinar
- “Prehistoric Genesis” conclusion
- Genesis prehistory and the End Times
Technically, this is the last installment of my “After the Dreams” series.
Mostly, I’m skipping over the Flood, because I’ve already written quite a lot about that. I will spend a bit of time on the aftermath of the Flood, but the main focus of this post is on the first half of Genesis 11, concentrating on the Tower of Babel and Nimrod. Those are two separate stories, but together I believe they present a good picture of the “last days”—globalism and world conflict!
The Flood
Genesis 6:9–8:19
This section of Moses’ narrative is separated from the previous by a very brief toledah.
Reminder–a toledah (pl. toledoth) in Moses’ writings is a short genealogy, introduced by “these are the generations of” and designed to separate two unrelated or loosely related topics.
10 And these are the generations of Noe [Noah]. Noe was a just man; being perfect in his generation, Noe was well-pleasing to God. 11 And Noe begot three sons, Sem, Cham, Japheth.
Genesis 6:10-11 (LXX-B)
I will not cover the flood in much detail here, because I have already written several articles on the subject. Click on the arrows to expand the embedded content:
Young Earth Creationism is currently dominated by followers of the late Henry M. Morris, who visualized the Great Flood as a cataclysmic worldwide flash flood with a supernatural volume of water falling mostly from heaven, and dried up by destructive high winds. This post presents a far more likely scenario for a global flood.
As much as I respect the folks who operate the Ark Encounter site in Kentucky, I disagree with almost every element of their depiction. Beginning with the giant ship model itself, which has anachronistic features; has features that wouldn’t work on a real ship; and by the way is by definition not by any stretch an ark!
From my own professional background, I know that there are a large number of geological features on earth that simply cannot be explained by a flood, whether regional or global in scope. Here I present a short list of examples.
In this post I examine Henry Morris’ lack of credentials for his claims about geology and the flood. I also explain my own background and how it bears on the subject.
We all know that the flood was God’s response to increasing corruption on the earth.
[11] Now the earth was corrupt in God’s sight, and the earth was filled with violence. [12] And God saw the earth, and behold, it was corrupt, for all flesh had corrupted their way on the earth. [13] And God said to Noah, “I have determined to make an end of all flesh, for the earth is filled with violence through them. Behold, I will destroy them with the earth.
—Genesis 6:11–13 (ESV) emphasis mine
That humans are capable of deliberate, rebellious sin is a result of Adam’s sin in the Garden. But the presence of major, outlandish, organized sin around the globe got its start from the example set by the rebellious angels and their offspring, the Nephilim, after which it was promulgated for millennia by the demon spirits of those same Nephilim.
If you think things are bad now, it was much worse in those days! But hang on, it is presently getting worse, not better. History is repeating itself.
This time, God will spare us another flood, just as He promised Noah. Instead, we will go straight to a modern Babel situation, which He will not stop this time. I believe that the new Nimrod, like Satan, is even now alive and well on Planet Earth…
After the Flood
Genesis 8:20–9:29
Noah’s offerings
20 Noach built an altar to ADONAI. Then he took from every clean animal and every clean bird, and he offered burnt offerings on the altar. 21 ADONAI smelled the sweet aroma, and ADONAI said in his heart, “I will never again curse the ground because of humankind, since the imaginings of a person’s heart are evil from his youth; nor will I ever again destroy all living things, as I have done. 22 So long as the earth exists, sowing time and harvest, cold and heat, summer and winter, and day and night will not cease.”
— Genesis 8:20-22 (CJB)
How did they know that?
Immediately after leaving the Ark, Noah and his family gave thanks to God by staging a massive burnt offering. The passage describing it, quoted above, seems entirely anachronistic in that it accords well with parts of the Torah sacrificial system, which was not announced until centuries in the future.
The Bible gives us absolutely no information on how the relevant instructions were delivered to pre-Sinai humanity. We know that God spoke directly to the Patriarchs. We also know that “angels” routinely spoke to humans—the Serpent, a cherub, spoke to Adam and Eve, and these two humans weren’t at all surprised. Evidently, they knew, or as it developed, thought that he was on God’s team.
The Ancient Near East produced a huge amount of lore regarding gods and demigods that frequently communicated with early humanity. In particular, Babylonian legends of the Apkallu imply to scholars like Michael Heiser that one of the pre-Flood sins of the Watchers was that they talked too much! By imparting arcane knowledge that caused civilization to advance at too rapid a pace, human pride became bloated and consciences seared.
Rather than speculate endlessly on how and why, let’s just examine this sacrifice…
The altar
Noah built an altar. (מִזְבֵּחַ mizbēaḥ, pronounced miz-BAY-akh), meaning a “place of sacrifice.” This is the first mention of a sacrificial altar in the Bible, though Abel may have prepared something equivalent for his offering.
The sacrificial animals
He offered every kind of clean land animal and clean bird. Noah had been told before the Flood to take with him seven pairs of each of the clean animals and one pair of each of the unclean. It is assumed, probably correctly, that the six extra pairs of clean beasts were for sacrificial purposes. God most likely did the collecting and herded the animals to the Ark, so how Noah knew which were clean and which were not is immaterial to what was actually done.
The offerings
Moses called them “burnt offerings.” Some scholars argue whether the burnt offering, here and later, was for reconciliation (forgiveness), atonement (temporary pardon) or thanksgiving, but they all miss the point.
In reality, it is none of the above. It was a promise of complete surrender and devotion to God, symbolized by completely burning up the animal sacrificed, except for the hide, which under Torah is donated to the priests.
Under Torah, a number of burnt offerings were offered up by priests for all the people or groups of the people, but individuals or families could provide their own animals and conduct their own sacrifices. Although other symbolism has been rightfully added to Christian baptism (particularly by Paul), I view baptism as preeminently identical in meaning to the individual burnt offerings.
Reformed churches, probably the majority of Protestants, equate baptism with circumcision, which is the reason they practice infant baptism. My soteriology is basically Reformed, but I reject pretty much all other distinctives of their theology, including their baptism.
God’s response
God smelled the “sweet (or pleasing) aroma.” Everyone who, like, me, enjoys a good steak, will agree that nothing smells better than freshly barbecued meat. To say that God “smells the sweet aroma“, or, in KJV, “the sweet savor”, is anthropomorphic. Biblically, it means that He is pleased with the offering and with the offeror.
God rewarded the offeror. Because He smelled the sweet aroma of Noah’s offering, God promised to “never again curse the ground…[or]…destroy all living things” because of the sins of mankind—Noah’s descendants.
Verse 22, in essence, promises that, as long as the earth remains, God will neither repeat nor add to the curse pronounced on the ground in Genesis 3. Specifically, He will not destroy the productivity of the ground.
Does the wording, “since the imaginings of a person’s heart are evil from his youth”, mean that God is excusing our sin? No, never, but it means that He understands that not all sin is committed with “malice aforethought.”
I think He cursed the ground in Genesis 3 because Adam’s sin brought to an end the prospect of spreading the idyllic conditions of the Garden to the outside world, and only a harsh environment would teach mankind skills needed to survive in a sin-cursed environment.
I also think that the rebellion of the Watchers and the spread of the Nephilim in Genesis 6 made a completely fresh start via the Flood unavoidable.
But now God makes allowance for hormones!
Do not confuse this promise with God’s covenant to not repeat the Flood.
The promise
“So long as the earth exists” in this verse implies that it will not always exist. While it does, we are promised that God will maintain for us the basic necessities for life on the planet. Pay attention, Gretta, there will be no more extinction events on earth!
How long will earth exist?
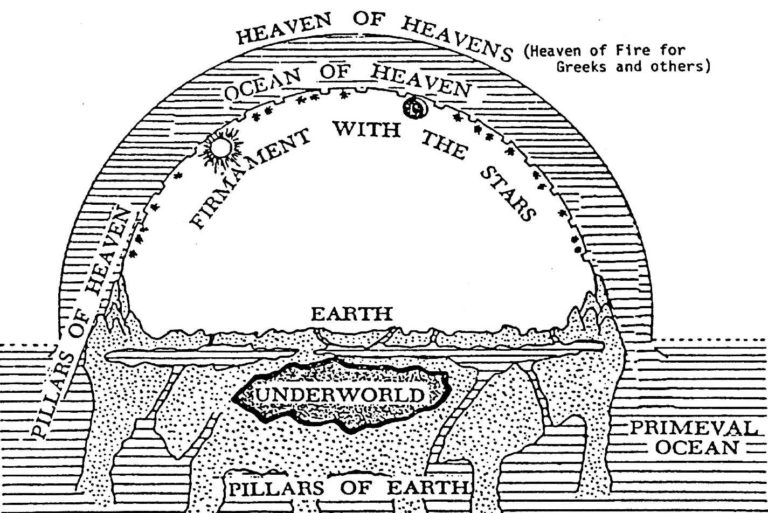
God and His celestial Host have no need of “homes.” In that sense, I don’t believe that “heaven” is a specific place. In 2 Corinthians 5:8, Paul suggest that when we as believers die, we will “be away from the body and at home with the Lord.” So, at that time, we too will be spirits, with no need of a “mansion over the hilltop.”
At the resurrection, though, we will acquire version 2.0 of our corporeal body, which will have physical needs. From that time, I believe that “heaven” for us will be a fully renovated earth with New Jerusalem hovering over it. As described in Revelation.
This will probably not last forever.
At about 4.6 billion years old, the sun is currently, but very slowly, expanding and getting hotter as it burns up the hydrogen fuel in its core, forming helium as a byproduct. Helium, being a heavier ion, migrates toward the center of the sun, gradually quenching the hydrogen reactions there. Through a complicated, but fairly well understood sequence, the helium, too, begins to burn and form still heavier ions. These heavier elements eventually begin burning as well.
About 5 billion years from now, the sun’s core will suddenly collapse, and its outer shells will simultaneously expand. It will become a huge “red giant” star, with Mercury, Venus, and possibly earth all swallowed up inside its volume. In yet another 10 billion years, another collapse will result in the sun becoming a very hot, but gradually dimming, “white dwarf” surrounded by a so-called “planetary nebula.”
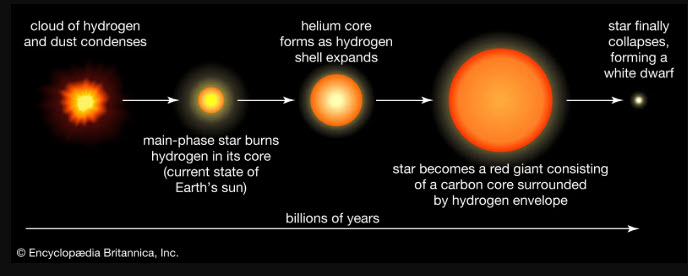
About a billion years from now, long before the red giant phase, earth will become uninhabitable. Never fear, though. God knows all this and has a plan. By that time, I’m sure we’ll all be ready to move to different quarters.
Man’s commission
Version 1.0 (looking back)
My readers know that I am an Old Earth Creationist, that I believe Day 6 in Genesis 1 was a prophetic view backwards at ancient animals and hominids that preceded the unique formation “from dust” of Adam in Genesis 2.
In the relevant Genesis 1 passage, God delivered a commission to pre-Adamic mankind:
28 God blessed them: God said to them, “Be fruitful, multiply, fill the earth and subdue it. Rule over the fish in the sea, the birds in the air and every living creature that crawls on the earth.” 29 Then God said, “Here! Throughout the whole earth I am giving you as food every seed-bearing plant and every tree with seed-bearing fruit. 30 And to every wild animal, bird in the air and creature crawling on the earth, in which there is a living soul, I am giving as food every kind of green plant.” And that is how it was. 31 God saw everything that he had made, and indeed it was very good.
— Genesis 1:28-31a (CJB)
Who precisely this commission was delivered to is unstated and irrelevant. It simply tells us the expectations that God had for the ancient peoples. He wanted them to rule and administer the earth, in much the same way that the angelic host rules and administers the rest of the universe.
It is obvious that God’s preference was that neither man nor beast should feast on flesh. But…
Did that have the force of command?
Probably not. God explicitly granted permission for man and beast to eat flora, but I see no actual prohibition against eating flesh. God sometimes allows things that He doesn’t prefer. You might say He’s a realist. Just the fact that He gave angels, men and animals “free will” guarantees the existence of sin. Even the inanimate universe has free will of a sort, in the face of quantum uncertainty.
Did God design animals and hominids as herbivores?
Perhaps He initially designed them to be herbivores, but the fossil record unambiguously shows that adaptation eventually produced meat eaters, and He let it happen. In fact, I believe that there are limits to what adaptation can achieve. Beyond those limits, surely God has to intervene, yet still we see species that can’t survive long on leaves alone.
One more objection has to be addressed:
The final phrase in verse 30 is “And that is how it was”, or “And it was so.” I confess that this reaches the absolute tip of my ability to translate Hebrew, but through research and digging at it, I have come to the conclusion that “and it was” is an incorrect translation of the Hebrew וַֽיְהִי, which better translators than I call a “Conjunctive waw verb of type Qal Consecutive Imperfect, 3rd person masculine singular.”
Very roughly, that means, “Given that A is true, then at some time in the future, B shall also be true.” If I am not precisely correct in phrasing it that way, then at least what I’m saying is that “and it was so” was not intended to present it as a done deal.
Finally,
“It was very good” means that God was happy with the results. Those who insist that “good” precludes death and mortality are engaging in specious arguments that second-guess the Creator!
Version 2.0 (looking ahead)
1 God blessed Noach and his sons and said to them, “Be fruitful, multiply and fill the earth. 2 The fear and dread of you will be upon every wild animal, every bird in the air, every creature populating the ground, and all the fish in the sea; they have been handed over to you. 3 Every moving thing that lives will be food for you; just as I gave you green plants before, so now I give you everything — 4 only flesh with its life, which is its blood, you are not to eat. 5 I will certainly demand an accounting for the blood of your lives: I will demand it from every animal and from every human being. I will demand from every human being an accounting for the life of his fellow human being. 6 Whoever sheds human blood, by a human being will his own blood be shed; for God made human beings in his image. 7 And you people, be fruitful, multiply, swarm on the earth and multiply on it.”
— Genesis 9:1-7 (CJB)
This version of the commission, given specifically through Noah, is a similar commission to “be fruitful, multiply and fill the earth”, but if differs in important respects:
Estrangement
While “subdue and rule” are implicit, this statement introduces an unpleasant, adversarial element that was totally absent before. There is animosity here that didn’t show through in Genesis 1. Instead of a peaceful co-residence on earth (and in Eden), we are now the enemy and enslaver of the animals.
Note that while granting explicit rights to exploit the animals, there is nothing here about “clean” vs. “unclean.” This suggests to me, once again, that God is drawing away from close fellowship with mankind in general. This will come to a head at Babel, where God separates mankind, while making provision for a People of His Own (see below).
The humans who I believe existed before the Garden were omnivorous, as are we, and so consumed meat, but wanton slaughter was probably rare or nonexistent. They were just another set of predatory species, among many.
What God intended for His Adamic line was fellowship between them and at least the animals formed after Adam in the Garden. Those animals were not made to be eaten or exploited!
Life outside the Garden was tough, by design, and I can’t imagine that Adam’s kin were vegetarian for very long. I am pretty sure that the corruption that developed later extended to all sorts of abuse of animals. The animals released from the Ark scattered with a dread of humans that never disappeared.
With the help of the rebellious Watchers and instigation by their demonic offspring, the Nephilim, the world from Jered to the Flood must have been totally dystopian and utterly barbaric.
What I think that God was communicating with Noah and his family here was, “I know that my flood was not the final word. I’ve given you an opportunity to regroup and establish some order, but humanity will always be corruptible. I know that you will continue to eat flesh, and I know I can’t stop that without destroying you, but I’m going to set a limit...
“All About that Blood”
Apologies to Meghan Trainor…
God stated emphatically, “You will not be allowed to consume the blood of animals, and you won’t be allowed to kill other humans at all.“ This is a symbolic prohibition to emphasize that critters aren’t veggies, and all life including animals, is sacred.
I do not at all agree with the common Dispensational claim that verse 6 is a charter for human government!
Together with verse 5, God is simply pronouncing a curse on any creature, man or beast, that sheds human life. There would be no more “mark of Cain” to protects killers from just vengeance.
God does not like human government! He permits it! Ideally, vengeance belongs to Him. We were created to recognize Him and Him alone as king. When the Israelite inhabitants of Canaan demanded a human king, God warned them that they would regret it.
The Noahic Covenant
8 Then God said to Noah and to his sons with him, 9 “Behold, I establish my covenant with you and your offspring after you, 10 and with every living creature that is with you, the birds, the livestock, and every beast of the earth with you, as many as came out of the ark; it is for every beast of the earth. 11 I establish my covenant with you, that never again shall all flesh be cut off by the waters of the flood, and never again shall there be a flood to destroy the earth.” 12 And God said, “This is the sign of the covenant that I make between me and you and every living creature that is with you, for all future generations: 13 I have set my bow in the cloud, and it shall be a sign of the covenant between me and the earth. 14 When I bring clouds over the earth and the bow is seen in the clouds, 15 I will remember my covenant that is between me and you and every living creature of all flesh. And the waters shall never again become a flood to destroy all flesh. 16 When the bow is in the clouds, I will see it and remember the everlasting covenant between God and every living creature of all flesh that is on the earth.” 17 God said to Noah, “This is the sign of the covenant that I have established between me and all flesh that is on the earth.”
— Genesis 9:8-17 (ESV)
God now established an important covenant, not with Israel, which didn’t yet exist, but with mankind as a whole (represented by Noah and his sons) and with animal life. No more global flooding.
Rainbows
In verses 9:12ff, God appointed the rainbow as a sign of His promise.
“Rainbow flags” don’t represent me or my views, but they also don’t profane God’s covenant with Noah, his family, and “every animal on earth.”
A sequence of colors on cloth is not “the sign of the covenant I am making between myself and you and every living creature with you, for all generations to come.”
Neither is a spectrum refracted from a prism. In fact, we may choose to call that spectrum a “rainbow”, but that isn’t the Biblical definition. Read God’s definition here, and don’t get so bent out of shape over some supposed misappropriation of a physical phenomenon:
13 I am putting my rainbow in the cloud — it will be there as a sign of the covenant between myself and the earth. 14 Whenever I bring clouds over the earth, and the rainbow is seen in the cloud; 15 I will remember my covenant which is between myself and you and every living creature of any kind; and the water will never again become a flood to destroy all living beings. 16 The rainbow will be in the cloud; so that when I look at it, I will remember the everlasting covenant between God and every living creature of any kind on the earth.”
— Genesis 9:13-16 (CJB) emphasis mine
I’ll point out also that God did not create rainbows at this time. He created them at the time He imbedded the laws of physics into the young universe. When a stream of photons is diffracted through a mist, a spectrum is cast. God told Noah, “When you or I see such a spectrum in the clouds under these conditions, from now on it will remind us both of my promise.”
The intoxication of Noah
18 The sons of Noah who went forth from the ark were Shem, Ham, and Japheth. (Ham was the father of Canaan.) 19 These three were the sons of Noah, and from these the people of the whole earth were dispersed.
20 Noah began to be a man of the soil, and he planted a vineyard. 21 He drank of the wine and became drunk and lay uncovered in his tent.
— Genesis 9:18-21 (ESV)
In view of what follows, we have to ask if there was a sin here? Wine consumption? Drunkenness? Nakedness in his tent?
I’ve written about alcohol before but not reached a firm conclusion. I’ve never been drunk, but almost everyone has, and I’m not willing to draw a firm conclusion here, either. Drunkenness obviously contributed to his nakedness, but not knowing what he was thinking of, by himself in his private quarters, I can’t judge that either.
The curse of Canaan
Perhaps the only sin here was in Hamm’s reaction. One has to think he was disrespectful to Noah.
Roughly speaking, after Babel Shem’s descendants spread throughout Mesopotamia, south into Arabia, and southeast into India. Ham’s descendants mostly ended up in northern and eastern Africa, as well as western Arabia and the southern Lavant. Japeth’s descendants tended to migrate westward into modern Europe, and north and northeast into Asia Minor and the Steppes.
Given those movements, how do we interpret the following?
22 And Ham, the father of Canaan, saw the nakedness of his father and told his two brothers outside. 23 Then Shem and Japheth took a garment, laid it on both their shoulders, and walked backward and covered the nakedness of their father. Their faces were turned backward, and they did not see their father’s nakedness. 24 When Noah awoke from his wine and knew what his youngest son had done to him, 25 he said, “Cursed be Canaan; a servant of servants shall he be to his brothers.”
26 He also said,
“Blessed be the LORD, the God of Shem;
and let Canaan be his servant.
27 May God enlarge Japheth,
and let him dwell in the tents of Shem,
and let Canaan be his servant.”
— Genesis 9:22-27 (ESV)
We have all heard of “the curse of Ham”, but it was not Ham who was cursed; it was very plainly Ham’s son, Canaan. Why Canaan and not Ham? It wasn’t God’s curse, it was Noah’s, and I suggest that Noah was thinking, “You disgraced your father, now your son will disgrace his father!”
Protestants in America and elsewhere, early colonial through Civil War, in an effort to make this passage “relevant” to the slavery debate then raging, read all kinds of self-serving nonsense into this passage. Though the racist element is largely gone from most of these churches, shabby theological processing has largely prevented reevaluation of the interpretations.
The three names mentioned in the passage, Canaan, Shem and Japheth, could be a reference to the actual three persons, or to their descendants. The latter is almost universally assumed, and that would probably be my assumption, too, except that I am viscerally opposed to basing doctrine on unproven assumptions. Either way, perhaps at some point Canaan did serve Shem and Japheth. It isn’t clear from history.
Given the preponderance of Hamite tribes in Africa, the temptation for pro-slavery Christians was to ignore the fact that Ham was not the cursed party and to posit that, by golly, Ham is the father of the black Africans, so God destined them to be slaves!
Clearly there is nothing to that interpretation, but honestly, it’s difficult to detect the curse in anything we know from Biblical or secular history. One thing we do know that might be relevant in some way is that God eventually took the land of the Canaanites and gave it to the Hebrews, a Semite tribe.
I’m not sure that it’s important that we even attempt to understand the content of the curse, in any case. It apparently wasn’t God’s curse. It was Noah’s, and I don’t think a curse uttered by a drunk or hungover Noah had any teeth.
Return to Shinar
Genesis 10:1–11:9
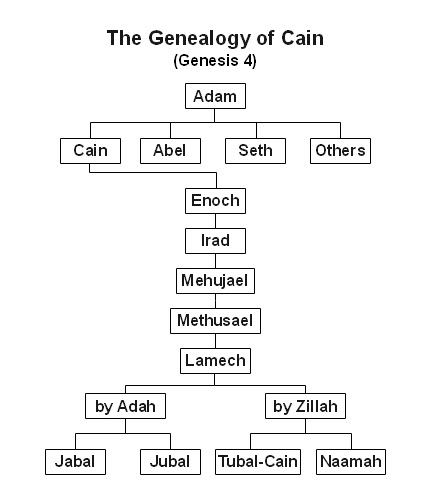
This is another section of Scripture that is little understood by Christianity at large but yet is vitally important in world history. It is a picture of human pride and globalist ambition.
The Toledah
Like all of the toledoth in Genesis, the one written in Genesis 10:1–39 is extremely informative and helpful to the Biblical historian. In my opinion, there is none more important for showing the pivotal role that the people listed played in early civilization and the development of all civilization to the present day.
The chart shown below is one of a large number showing graphically the data of the toledah. I elected to use this one because its columnar format emphasizes the generational development of ancient society. The date ranges at the top put it into a useful perspective, but I’m not at all convinced of their accuracy, as I will discuss below.
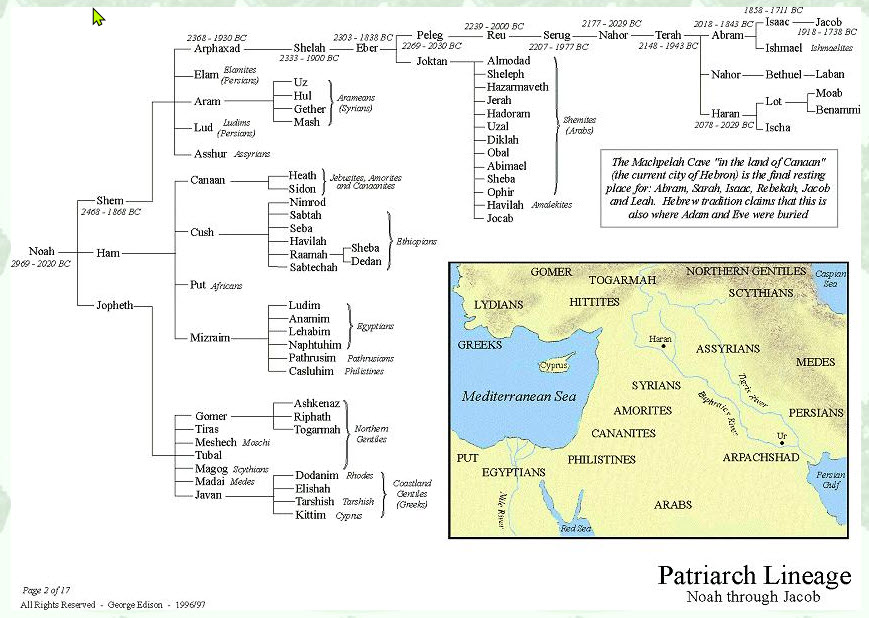
I’ll make just a few comments on the data as introduction for the final two sections of this post:
- Note that the first name entry at the top of each column is the direct patriarchal lineage from Noah to Jacob.
- Verses 4 and 5, concern Japeth’s grandsons via Gomer. The language in verse 5 refers to the dispersion at Babel, which I’ll discuss in some detail below.
From these were the islands of the Gentiles divided in their land, each according to his tongue, in their tribes and in their nations.
— Genesis 10:5 (LXX-B)
- Verse 6 lists the sons of Ham, “Kush, Mitzrayim, Put and Kena‘an.” Anglicized, those are Cush, Egypt, Put and Canaan. Those names are easily associated with the Nile Valley, the Eastern Sahara, and north into the Lavant.
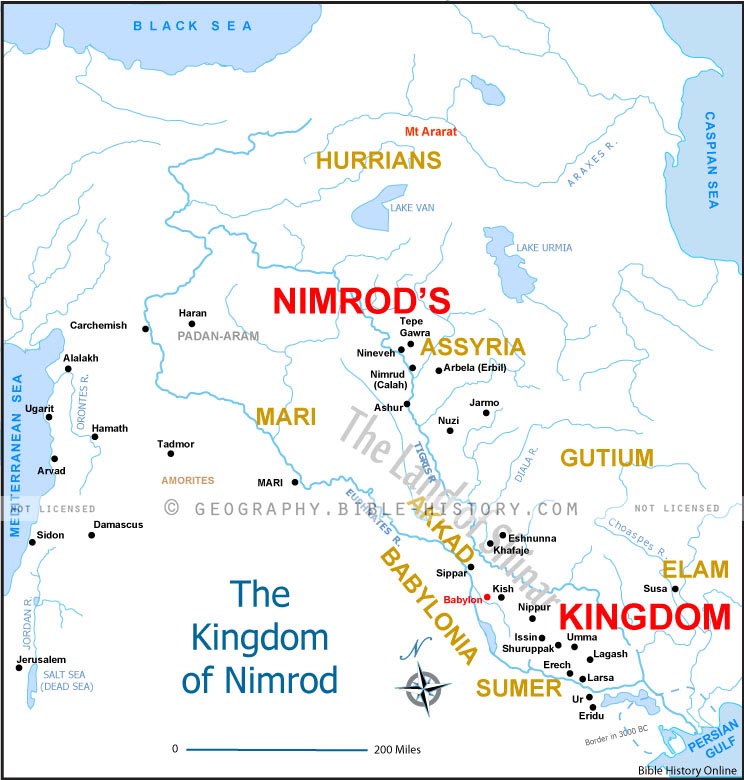
Cush, though, is a bit more complicated. Most scholars recognize that name as applying to the region of Somalia, Eretria, and Ethiopia, but I believe that Cush and his offspring also settled a large area of central Mesopotamia and eastward, well into India. - According to verse 8, “Kush fathered Nimrod”, the subject of the last major section of this post. Christian tradition credits Nimrod with founding Babel and building the Tower. Verse 10, however, only credits him with being king of Babel early in his life. I think that Nimrod most likely had nothing to do with building the tower. See below.
- Some translations render verse 11 as, “Ashur went out from that land and built [Nineveh], [et al]”, but in context, a better translation would probably be, “From [Babel] he [Nimrod] went into Assyria and built Nineveh, [et al].”
- Verses 15–20 list a number Canaan’s sons, some of whom you will recognize as the names of tribes that Joshua fought during the Conquest years.
- Verses 21ff mention a 3rd-great-grandson of Shem, Peleg, a name that means “to split or divide.” He got that name because, “in his days the earth was divided…”. Again, see below.
I’ve seen the silly suggestion by a Young Earth Creationist that verse 25 refers to a time after the Flood when God broke up the primordial supercontinent, Pangea, into the present scattered continents. Sorry, no! That statement can only refer to the dividing of the nations’ inheritance at Babel, Moses’ very next topic. - Peleg’s father, Eber, is the man from whom the clan-name “Hebrew” is derived.
Babel
Migratory beginnings
I imagine that it probably took many years for the sea level to return to its pre-Flood normal. In that regard, we were told in the Flood story itself:
1 But God remembered Noah and all the beasts and all the livestock that were with him in the ark. And God made a wind blow over the earth, and the waters subsided (שְׁכַךְ, shakak, “were caused to abate”). 2 The fountains of the deep and the windows of the heavens were closed, the rain from the heavens was restrained, 3 and the waters receded (שׁוּב, shub, “to turn back or retreat”) from the earth continually. At the end of 150 days the waters had abated (חָסֵר, chaser, “to decrease or make lower”), 4 and in the seventh month, on the seventeenth day of the month, the ark came to rest on the mountains of Ararat. 5 And the waters continued to abate (chaser again) until the tenth month; in the tenth month, on the first day of the month, the tops of the mountains were seen.
6 At the end of forty days Noah opened the window of the ark that he had made 7 and sent forth a raven. It went to and fro until the waters were dried up from the earth. 8 Then he sent forth a dove from him, to see if the waters had subsided ( קָלַל, qalal, a very linguistically fluid term that here seems to imply that the flooding was a relative trifle compared to what it had been) from the face of the ground. 9 But the dove found no place to set her foot, and she returned to him to the ark, for the waters were still on the face of the whole earth. So he put out his hand and took her and brought her into the ark with him. 10 He waited another seven days, and again he sent forth the dove out of the ark. 11 And the dove came back to him in the evening, and behold, in her mouth was a freshly plucked olive leaf. So Noah knew that the waters had subsided from the earth. 12 Then he waited another seven days and sent forth the dove, and she did not return to him anymore.
13 In the six hundred and first year [of Noah’s life], in the first month, the first day of the month, the waters were dried (חָרַב, charab, “To be dry, to be desolate, to lay waste, to destroy”) from off the earth (הָאָ֑רֶץ, ha-aretz, usually means a portion of the earth or land mass, not the whole). And Noah removed the covering of the ark and looked, and behold, the face of the ground was dry (charab again). 14 In the second month, on the twenty-seventh day of the month, the earth had dried out (יָבֵשׁ, yabesh, “dried up, seared, withered”).
— Genesis 8:1-14 (ESV) emphasis and explanation mine
In that passage, none of the underlined terms for the receding flood imply a completed process.
Because Moses wrote the Flood story in the form of a highly structured symmetrical poem, interpreting the sequence of its phases as described in Genesis 7 and 8 is extremely difficult. The following table from World Bible Commentary does it as well as I think it can be done.
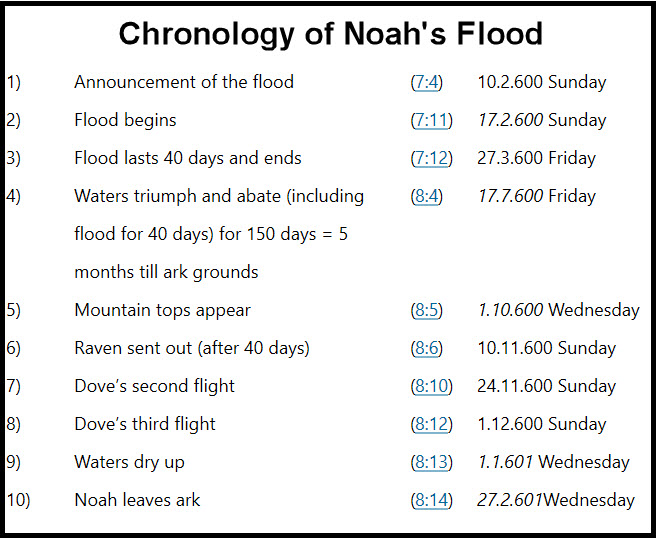
The column on the right is an attempt at dating the events—format: day.month.ageNoah
Dates in italics are from the text; other dates are interpreted.
From the start of the deluge until Noah left the Ark was a year and 10 days. Apparently, it took only 40 days for the water to rise to its peak, 45 feet above the highest mountain. It then took about 6½ months to drop the flood level by those 45 feet, and nearly 5 more months before they could safely leave the Ark.
What I envision is that at the close of this period, the ground in the highlands of Armenia around the Ark’s resting place had dried out, but the lowland plains and the lower reaches of the mountains were most likely still submerged. Surely God could have removed the excess water instantaneously, but I don’t think it is ever good exegesis to assume more than is stated. See God with the Wind for the significance of God’s wind in Scripture.
I think it likely that Noah’s family hung around the Ark while long distance travel was greatly impeded. Then perhaps years later, as plant life reemerged in the wake of the falling water, it became easier to move, and they began scattering along the highlands and living as nomads over a larger and larger range.
Babel colonized
1 Now the whole earth had one language and the same words. 2 And as people migrated from the east, they found a plain in the land of Shinar and settled there. 3 And they said to one another, “Come, let us make bricks, and burn them thoroughly.” And they had brick for stone, and bitumen for mortar. 4 Then they said, “Come, let us build ourselves a city and a tower with its top in the heavens, and let us make a name for ourselves, lest we be dispersed over the face of the whole earth.”
— Genesis 11:1-4 (ESV)
Note that “everybody speaking the same language” doesn’t necessarily mean that “all the earth (or land)” lived in the same place. That is an assumption from verse 1, but the Hebrew בְּנָסְעָ֣ם in verse 2 translates to “as they (3rd person masculine plural) journeyed, traveled, or moved.” The ESV translators chose not to assume that “everyone” in verse 1 traveled together in verse 2, saying merely that “people migrated.”
Nor does “speaking the same language” imply that dialectical differences had not developed. Only that they could still understand each other. Language drift is normal over long periods of time.
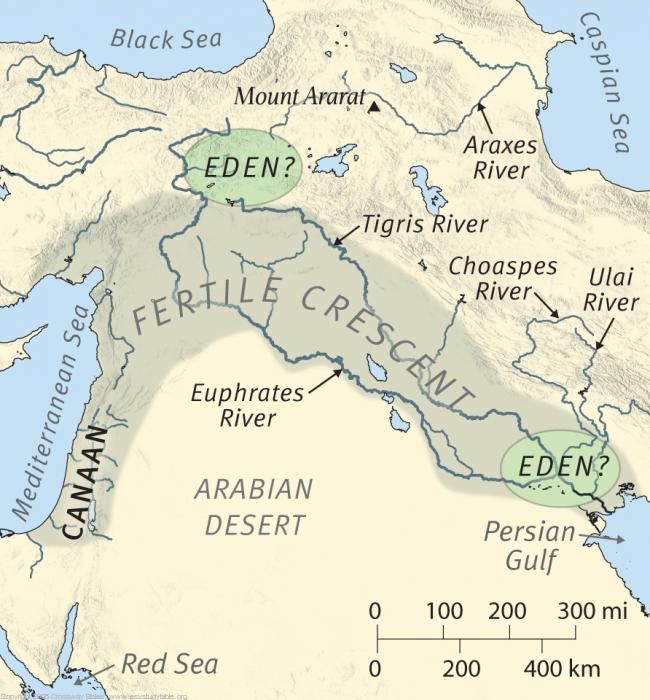
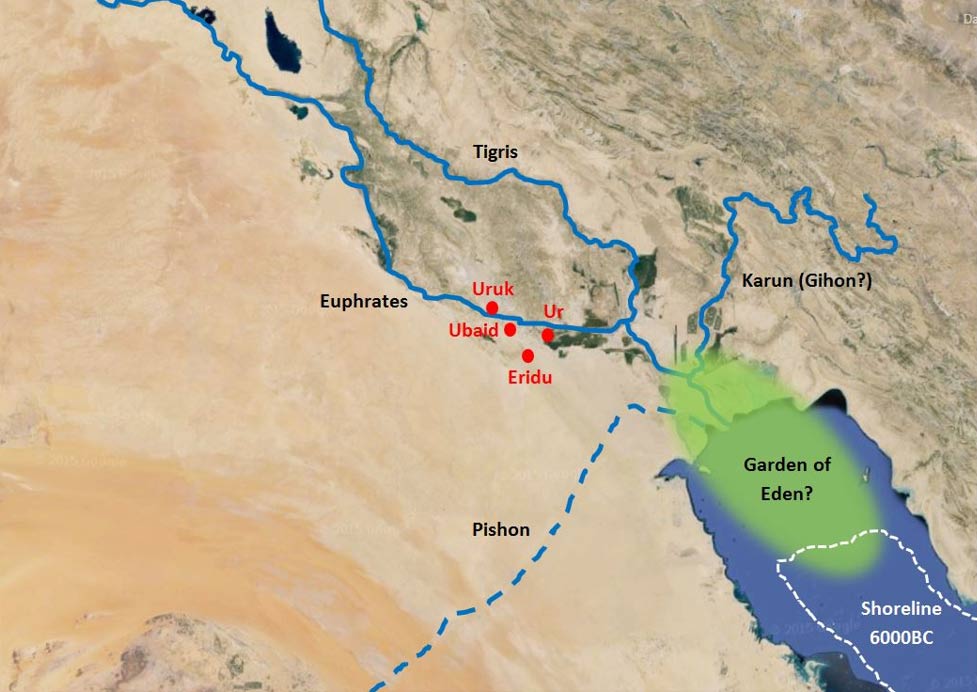
Eventually, at least one group of them made its way down the Zagros Mountains in today’s western Iran and noticed the lush plain below. They had rediscovered Shinar, the ancient region of the Garden. This area is probably the area known to secular history as Sumer, in southern Mesopotamia near the Persian Gulf. The Gulf probably extended farther north then, as shown in gray on the following map.

Sooner or later, some of these hunter-gatherers and nomadic farmers and herdsmen decided to settle down. Settling down involves permanent structures, commerce, and usually religion. Babel was the city they founded. I now think that Babel was the ancient city of Eridu (see below), which is much farther south than I showed it on the migration map.
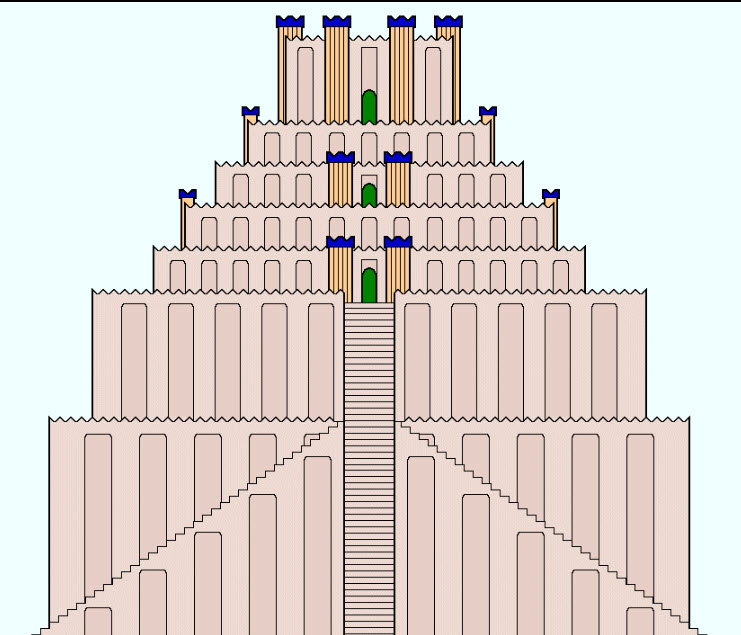
The Tower
When the Flood survivors left the region of Ararat, they probably did not all travel together. They fanned out. By the time of Peleg, humanity has been “fruitful” for generations. They have become tribal and competitive. When tribes meet, they probably fight. Babel may or may not have been the first city built after the Flood, but by then, mud bricks had clearly been invented and brick structures erected.
By that time Yahweh was once again mostly forgotten. The settlers in Shinar recalled distorted stories of the ancient “gods” who created the world and later destroyed it again in a flood.
Many Christian archaeologists believe that the Tower of Babel was the ancient Babylonian Ziggurat of Etemenanki. Babylon is probably way too far north to be ancient Babel, though. According to Dr. Petrovich (see below), Babel was probably the ancient Eridu. However, there were eventually many ziggurats, and each had similar design.
Those who scoff at the “ancient fools who thought they could build a tower all the way to heaven” are overthinking the story. The goal, as stated, was to build, “a city and a tower with its top in the heavens.” To the ancient people, that just means tall! The tower was to be as tall as they could build it, not to leave the planet and reach the god in heaven, but to attract him to a nice penthouse in the city. The top tier of a ziggurat was a small chapel with a bed and other accouterments suitable for a god and his consort to hang out in.
The ultimate goal at Babel was that the city and tower together would be so impressive that they, and the threat of a resident protector god, would discourage marauders (their kin who left Ararat in different directions) from attacking them and driving them out.
Wikipedia, of course, calls the Tower of Babel a myth, but without the mile-high space needle that most people envision, this is just a normal piece of history. The concept of building a tall tower to attract the god and impress enemies made perfect sense. By their perspective, the tower did indeed reach into the heavens.
But what Yahweh saw was arrogance and more rebellion!
In support of Eridu as the city of Babel, a Sumerian myth called Enmerkar and the Lord of Aratta presents a parallel account of Babel. It states that, “Enki … Lord of Eridu, changed the languages in their mouths, as many as he had put there, the languages of mankind, which were one.”
The scattering
Following is an English translation from the Septuagint, the Greek Old Testament that 1st century Jews in Judea used:
6 And the Lord said, Behold, there is one race, and one lip of all, and they have begun to do this, and now nothing shall fail from them of all that they may have undertaken to do. 7 Come, and having gone down let us there confound their tongue, that they may not understand each the voice of his neighbor. 8 And the Lord scattered them thence over the face of all the earth, and they left off building the city and the tower. 9 On this account its name was called Confusion, because there the Lord confounded the languages of all the earth, and thence the Lord scattered them upon the face of all the earth.
— Genesis 11:6-9 (LXX-B)
For the third time in Genesis, we see Yahweh speaking to His angelic Divine Council: “Let us…” This is certainly not the Trinity conferring together. What one thinks, they all know. It is the triune God speaking to His Divine Council.
To review:
The Divine Council is a panel of probably 24 high-ranking angelic spirits, seen in several Biblical prophetic visions on secondary thrones around Yahweh’s throne. As explained in Gods and Demons, the function of this council was to assist Yahweh in administration of the created universe. Not because He needs help, but because He values their fellowship.
As stated above, language drift is ongoing over time, so there were probably dialect differences from place to place, but everyone could understand each other. After God’s action, different peoples in different areas ended up with incompatible languages. Presumably this division was along clan lines.
One takeaway from this story is that God does not value human globalism or multi-culturalism. In a reverse of wedding ritual, one might say, “what God has ripped asunder, let no man join together.”
Another consequence
Aside from confusion of tongues, something else of huge importance happened at the Babel scattering. There are hints throughout Scripture, particularly in Daniel and the writings of Paul, that the nations of the world are supervised in some way by angelic “princes.”
Moses doesn’t mention it here in Genesis, but he does in his final statement, delivered at the foot of Mt. Nebo and known as “The Song of Moses.”
8 When the Most High gave to the nations their inheritance,
when he divided mankind,
he fixed the borders of the peoples
according to the number of the sons of God.
9 But the LORD’S portion is his people,
Jacob his allotted heritage.
— Deuteronomy 32:8-9 (ESV)
“Prehistoric Genesis” conclusion
We have now reached the end of my chronological coverage of what I have dubbed, “Prehistoric Genesis”, which more or less ends with Genesis 11:9. I want to wrap up the series by discussing three additional topics from Genesis 1–11 that rightfully belong to what I call the historical part of Genesis, but that tie the historical to the prehistorical.
Nimrod
The toledah of Genesis 10 served as both:
- a “cinematic fadeout” to chronologically separate the Flood story from the Babel story, both of which I view as of essentially equal theological importance; and
- a “clan-centric” view of humanity going into Babel and the separating of nations.
The language of sonship
Embedded in that toledah and arguably out of chronological sequence is a brief discussion of Nimrod:
6 The sons (וּבְנֵ֖י, ubəne, literally, “and the sons”) of Ham: Cush, Egypt, Put, and Canaan. 7 The sons of Cush: Seba, Havilah, Sabtah, Raamah, and Sabteca. The sons of Raamah: Sheba and Dedan. 8 Cush fathered (יָלַד, yalad, “begat”) Nimrod; he was the first on earth to be a mighty man. 9 He was a mighty hunter before the LORD. Therefore it is said, “Like Nimrod a mighty hunter before the LORD.” 10 The beginning of his kingdom was Babel, Erech, Accad, and Calneh, in the land of Shinar. 11 From that land he went into Assyria and built Nineveh, Rehoboth-Ir, Calah, and 12 Resen between Nineveh and Calah; that is the great city.
— Genesis 10:6-12 (ESV)
From this genealogy, you see that Cush had five sons (וּבְנֵ֖י, ubene, “and the sons”) and at least a couple grandsons. But then Nimrod is mentioned separately from the other sons, and using a different term: Yalad, the familiar “begat“, or rendered as “fathered” above. Yalad is used around 490 times in the Old Testament, and like many Hebrew words, it has a broad range of related meanings. Here is a sampling:
- Mostly the word is used to establish a line of descent, as A begat B, who begat C, who begat D, etc.
- It can also skip generations if those coming in between are irrelevant to the discussion, as A begat D.
- It can also be said of motherhood, as the wife of A begat B.
- It can be used of animals, as Cow begat calf.
- A midwife can be said to beget a child she helps deliver.
- Godly kings have been said to be begotten of God, a symbolic relationship.
- God says that He begot Israel, again symbolic.
- Of course, the Son, Jesus, is begotten of the Father. This is again symbolic, because the eternal Son was never literally born.
Given the above, Nimrod may possibly have been a remote descendant of Cush, not a literal son.
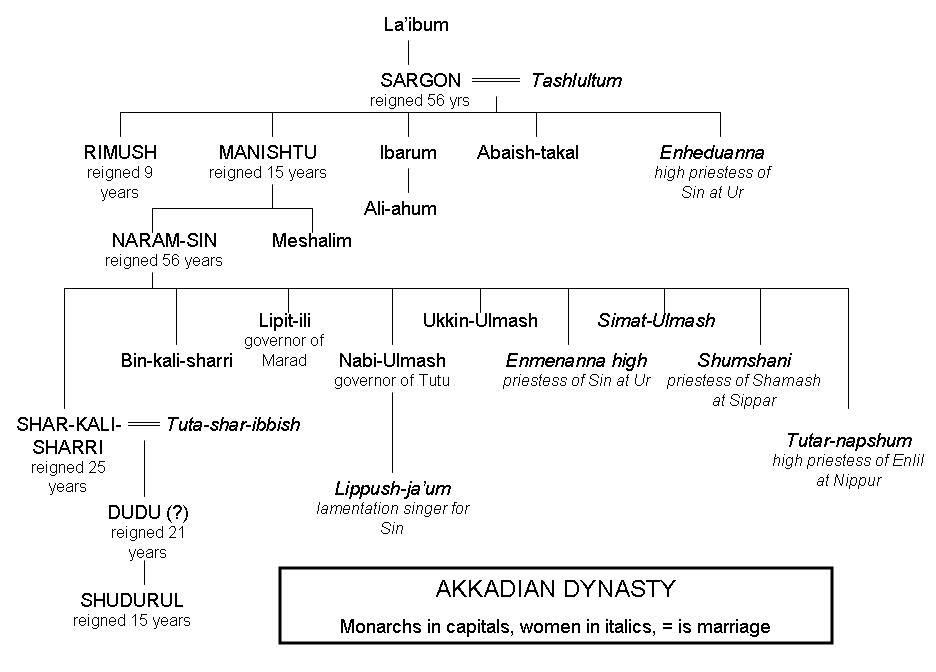
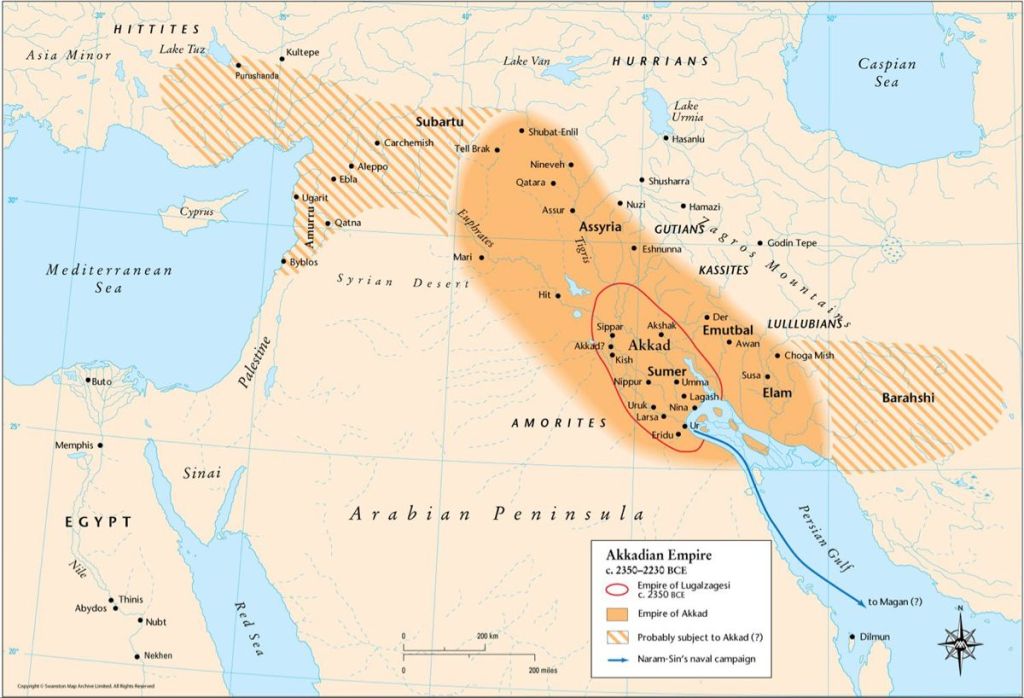
In his 2023 Book, Nimrod the Empire Builder: Architect of Shock and Awe, Dr. Douglas Petrovich of Brookes Bible College has shown, fairly conclusively in my opinion, that Nimrod was none other than Sargon of Akkad, aka, Sargon the Great.
Why ancient Biblical dates are unreliable
Not all of Dr. Petrovich’s arguments are clear. He thinks that Sargon’s reign was generations later than the Scattering, but he doesn’t provide much in the way of date evidence.
The fact is that all dates that far back in time are questionable. Ancient peoples did not have a continuous calendar like our Gregorian. Secular dating is limited to archaeological and philological data that may be very unclear. Biblical dating is better, but subject to misinterpretation of “begats”, for example.
Sargon is a historical figure whose reign is dated roughly to 2334–2279 BC. How does that match with allusions to the Scattering in Genesis 10? Referring to the chart below, Peleg was apparently contemporary with Sargon but died shortly before Sargon’s accession as King of Akkad. But since it seems the Scattering occurred during the time of Peleg, how could Sargon have come decades later as Petrovich contends?
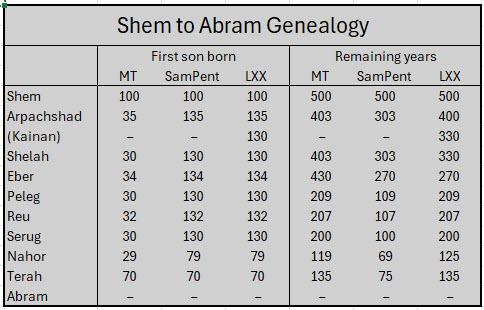
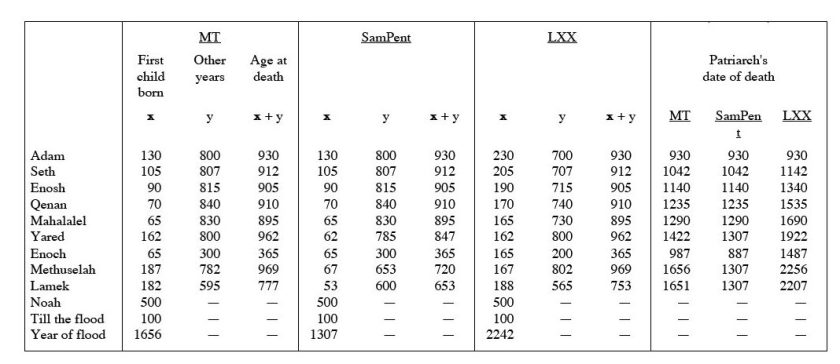
To address that question, I decided to do a comparison of the ages of Shem’s descendants in the Masoretic, as compared to the Septuagint (LXX) and the Samaritan Pentateuch (SamPent).
In my last post, I presented a similar chart, from World Bible Commentary, for Seth’s descendants. WBC provided something similar for this period but presented less data, and it contained numerous errors. So, I felt compelled to do my own chart, which meant digging into the Hebrew language source documents.
Sure enough, I find that there are major discrepancies between these source documents, though the differences aren’t quite the same as WBC presented before. If one uses the SamPent and LXX numbers instead of MT, it changes a lot of genealogical charts done over the centuries.
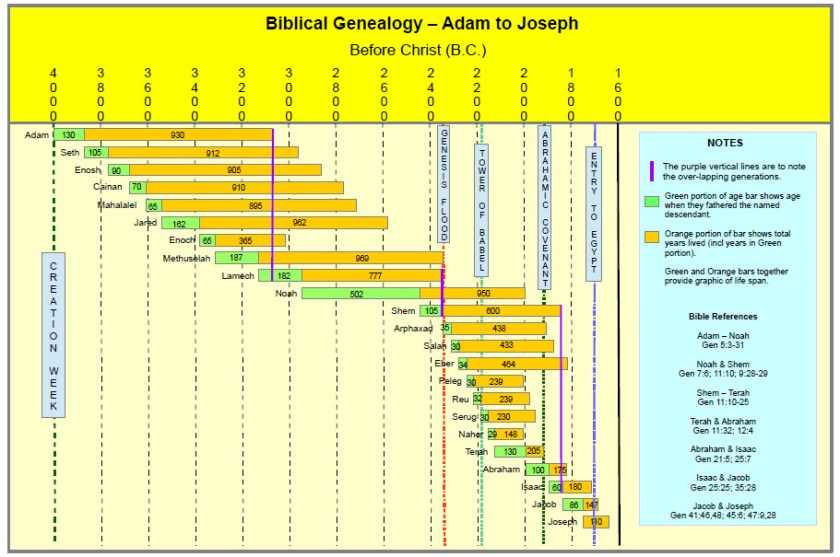
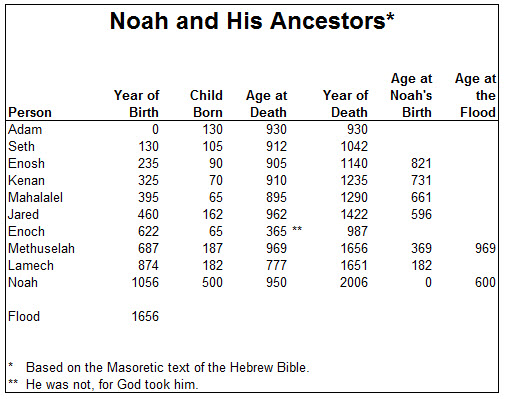
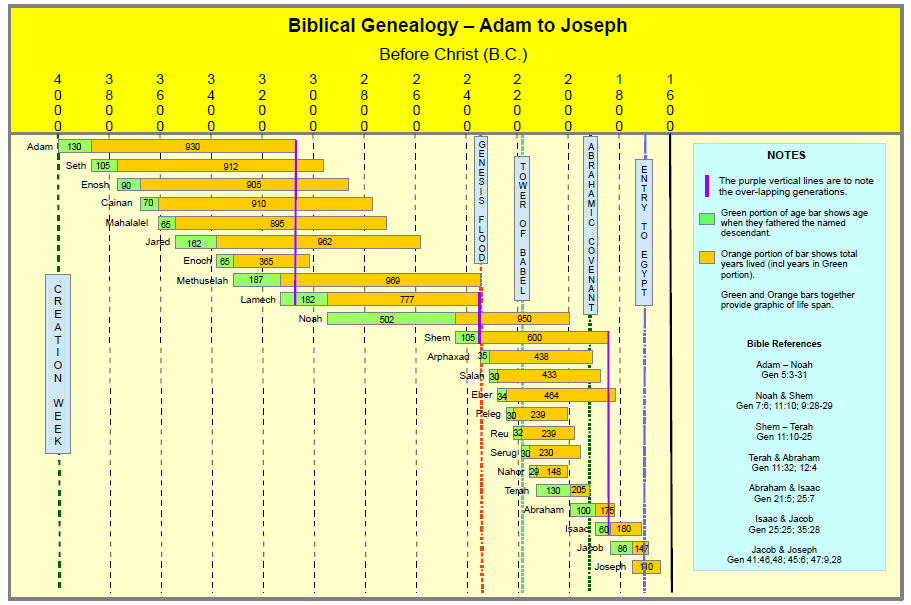
Archbishop Ussher calculated the date of the “creation week” by starting with an assumed known date, say, the approximate date of Joseph’s entry into Egypt when he was sold into slavery at 17 years old; and then, using something like the Adam to Joseph Genealogy, above, to add up the ages of the fathers at first son’s birth to count back to Adam’s creation. When he did this using Masoretic dating, he came up with a creation date of 4004 BC.
But what if the ages recorded in the Masoretic text are wrong? Then the calculation is incorrect. My charted numbers for this period are mostly consistent for SamPent and LXX, but the MT numbers are a hundred years shorter. Also, LXX introduces another generation, Kainan, that the others skip. Using these bigger numbers pushes Adam’s “birth” and the Flood back many centuries.
So, which is true? Christian inerrantists like me would prefer for everything in the Bible to be crystal clear and unambiguous, but that just isn’t the way it is. Consider the following:
- Aside from the folks who believe that KJV is an inerrant translation, even most Young Earth Creationists understand that the “begats” might skip over some generations.
- It seems obvious to me that there are numerous roundoffs in the age data, some to the nearest five years, and some to the nearest hundred!
- In Gen 5:32, Noah was 500 years old when he fathered Shem. In 7:16, he was 600 at the Flood. But in 11:10, Shem fathered Arpachshad when he was 100, two years after the flood. The 2-year discrepancy is simple round-off error, but it really troubles some Christian writers.
And also, regarding the source texts:
- Most English translations are based on the Masoretic text because it is a compendium of what for centuries were the only available Hebrew manuscripts.
- In general, older texts and fragments are considered more trustworthy because until Gutenberg, all copies were done by hand and therefore subject to copy errors.
- The SamPent is a risky source because it was edited for sectarian purposes.
- The LXX is a Greek translation of one or more older Hebrew texts that are no longer extant. It has to be considered accurate, because it was the Old Testament used by Jesus and the NT writers, but the Greek language obscures some of the Hebrew terminology and nuance.
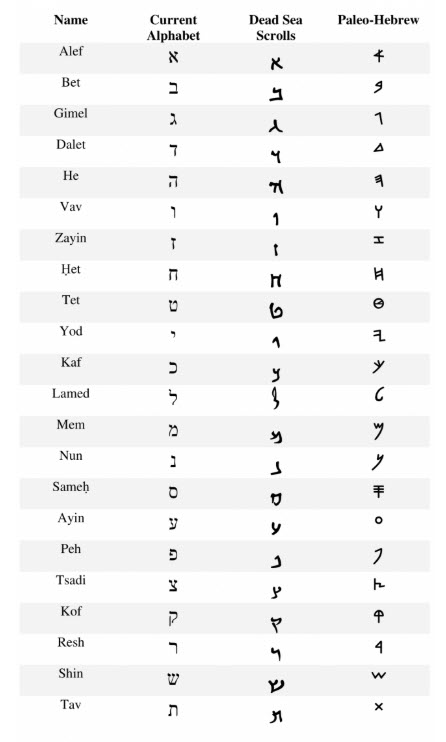
- The Hebrew language has no numerals. Instead, like Roman Numerals, Hebrew assigns numeric values to the Hebrew letters. For example, yesterday (as I write) was the Hebrew “New Year of the Trees”, TU B’Shevat. The “T” is Hebrew letter tet, with a value of 9, and the “U” is Vav, with a value of 6.
9 + 6 = 15, so TU B’Shevat literally refers to the date 16 Shevat. - The Masoretic OT text is even more complicated. In Gen 11:12, the number 35 appears in a more primitive form, spelled out, as חָמֵ֥שׁ וּשְׁלֹשִׁ֖ים, which translates as “five and thirty.”
- The same verse in the SamPent and (presumably) the source for the LXX, reads “five and three and hundred years”. One wonders if some key medieval scribe copyist working on the Masoretic text didn’t think the “and hundred” entry (ומאת) was nonsense, where it appeared, and dropped it.
Whatever the reason(s) for the mismatched age data, in my opinion scholars should abandon attempts to compute accurate dates from it, because quantitative results can only be guesses.
Since Shem and Ham were brothers, Cush was probably in the same generation as Arphaxad. Note that if Nimrod was a direct son of Cush, then he would have been roughly contemporary with Shelach, much too early to have been Sargon.
Sargon of Akkad
Because of age discrepancies in the source texts, it is a step too far for me to say that dates compiled from the toledoth prove that Nimrod lived generations after Peleg. What those discrepancies do allow me to say is that it is possible.
Petrovich offers two other lines of support for Nimrod as Sargon.
The characters of Nimrod and Sargon
Moses wrote, “10:8b [Nimrod] was the first on earth to be a mighty man. 9 He was a mighty hunter before the LORD.” As translated, this sounds like a complimentary description of an admired hunter and hero, but Dr. Petrovich takes issue with a number of choices made in the translation. His reasoning is too complicated to repeat here, but the bottom line is that:
- “He was the first on earth to be a mighty man” should be rendered as something akin to “He acted in a profane manner in his quest to become powerful on earth.”
- “He was a mighty hunter before the LORD” should be “He was a brutal slaughterer before the LORD.”
In other words, far from being an admired hunter of game, he was a feared and ungodly butcher of men. Like most conquerors. Like Sargon.
The conquests of Nimrod and Sargon
Moses is presenting Nimrod as the first empire-builder in history, which is Sargon’s claim to fame in secular histories. Verses 10:10–11 list cities conquered by Nimrod, beginning at Eridu (Babel?) and moving northwest in Sumer (Shinar?), then north of that into Assyria. This is the basic pattern followed by Sargon. See the two maps that follow.
A final toledah
This is the genealogy of Abram/Abraham, covering his patriarchal line up to Shem. I quote it here in full because of its importance.
10 Here is the genealogy of Shem. Shem was 100 years old when he fathered Arpakhshad two years after the flood. 11 After Arpakhshad was born, Shem lived another 500 years and had sons and daughters.
12 Arpakhshad lived thirty-five years and fathered Shelach. 13 After Shelach was born, Arpakhshad lived another 403 years and had sons and daughters.
14 Shelach lived thirty years and fathered ‘Ever. 15 After ‘Ever was born, Shelach lived another 403 years and had sons and daughters.
16 ‘Ever lived thirty-four years and fathered Peleg. 17 After Peleg was born, ‘Ever lived another 430 years and had sons and daughters.
18 Peleg lived thirty years and fathered Re‘u. 19 After Re‘u was born, Peleg lived another 209 years and had sons and daughters.
20 Re‘u lived thirty-two years and fathered S’rug. 21 After S’rug was born, Re’u lived another 207 years and had sons and daughters.
22 S’rug lived thirty years and fathered Nachor. 23 After Nachor was born, S’rug lived another 200 years and had sons and daughters.
24 Nachor lived twenty-nine years and fathered Terach. 25 After Terach was born, Nachor lived another 119 years and had sons and daughters.
26 Terach lived seventy years and fathered Avram, Nachor and Haran. 27 Here is the genealogy of Terach. Terach fathered Avram, Nachor and Haran; and Haran fathered Lot. 28 Haran died before his father Terach in the land where he was born, in Ur of the Kasdim.
— Genesis 11:10-28 (CJB)
We already know that the scattering from Babel happened in the lifetime of Peleg. Since this provides no additional information on that, we still don’t know if Peleg was physically in Babel when it happened, or who the leader or leaders of the city at that time were. Peleg is only a marker for us.
Abram’s calling
29 Then Avram and Nachor took wives for themselves. The name of Avram’s wife was Sarai, and the name of Nachor’s wife was Milkah the daughter of Haran. He was the father of Milkah and of Yiskah. 30 Sarai was barren — she had no child. 31 Terach took his son Avram, his son Haran’s son Lot, and Sarai his daughter-in-law, his son Avram’s wife; and they left Ur of the Kasdim to go to the land of Kena‘an. But when they came to Haran, they stayed there. 32 Terach lived 205 years, and he died in Haran.
— Genesis 11:29-32 (CJB)
The martyred deacon, Steven, gave a more detailed account of Abraham’s early movements than did Moses. This was without doubt from lore passed down verbally.
2 and Stephen said:
“Brothers and fathers, listen to me! The God of glory appeared to Avraham avinu (Abraham our father) in Mesopotamia before he lived in Haran 3 and said to him, ‘Leave your land and your family, and go into the land that I will show you.’ 4 So he left the land of the Chaldeans and lived in Haran. After his father died, God made him move to this land where you are living now.
— Acts 7:2-4 (CJB)
Genesis prehistory and the End Times
Most Christians are interested in Creation, the Garden of Eden and the Flood. Most are not interested, particularly, in the genealogies, the millennium between Cain and Abel and the Flood, or the millennium between the Flood and Abraham. Thinking about these old things to most is like watching old Black and White Japanese Godzilla movies on TV. It’s just the “weird part of the Bible”. Monster stories for kids’ comic books.
Well, what’s it even there for?
First of all, for the ancient Israelites, coming out of the pagan Egyptian culture and preparing to enter the pagan Canaanite lands, it was a polemic against all they had been taught since childhood.
All the stories were familiar, but the heroes weren’t the pagan gods and kings they’d always been taught to revere. Yahweh was infinitely greater, more powerful, and more benevolent than any of them.
For the Israelites about to cross the Jordan, He is the God who can control the most powerful forces of nature, He can wipe out all life on earth if He chooses, and He can scatter and isolate all humanity to quell rebellion.
And while He alone is the personal God of His chosen people, He has placed all other peoples under the rule of angelic overseers that He created. Although they became corrupt over time and presented themselves as gods, they serve His purposes and He can easily control them as He desires.
The same lessons are there for all other peoples of all times, both those among His elect and those who are not.
But there is another layer to this that applies to those of us living in the acharit hyamim, the End of Days..
The Serpent is still the Deceiver and the Accuser. He still has his hordes of rebellious celestial spirits and the temporarily dormant demonic Nephilim spirits.
As it was in the days of Noah, hedonism and rebellion against God are on the rise. Yahweh promised never again to destroy all flesh, but even after the flood, mankind plotted to unite in rebellion. Though He scattered them and divided them, countless Nimrods have attempted to once again unite the world against Him.
Modern rulers, through technology, persuasion, and economic globalism have renewed the effort to build a “tower to heaven”, and it is only a matter of time before a new Nimrod rises to “take control” in the name of peace and prosperity.