Outline:
Which came first?
Common origin?
What constitutes a myth?
The Egyptian creation myth
The Bible’s use of non-Biblical sources
Yes, indeed it does! Contemporary scholarship is aware of many, many undeniable similarities between historical events, cultural traditions, and even cultic practices (temple construction and ritual) as recorded in the Bible and those recorded in the sometimes-earlier legends of various ancient pagan civilizations. Does this mean that the Biblical material is stolen, copied, or derived from pagan sources? Is the Hebrew Bible copycat literature? If so, should we question the Bible’s inspiration, inerrancy and authority?

Which came first?
There may be copying, but it isn’t always clear who copied whom.
Most of you will have either heard or read somewhere that the Genesis Flood story is similar to pagan legends such as the ancient Gilgamesh Flood Myth. Since “everyone knows” that the pagan work is mythological and came first, then “surely the Biblical record must be mythological as well, and so it should not be believed by intelligent people.” The Hebrew Bible is copycat literature, right? Plagiarized!
Did the Babylonian Flood Myth really precede the writing of Genesis? The pagan myth resides primarily on Tablet 11 (of 12) of the Standard Babylonian Version of the Epic of Gilgamesh, which contains gaps (lacunae) but is the most complete version known. This version is dated to the period 1300–1000 BC. Wikipedia claims that this is hundreds of years before Genesis was written, but by conservative Evangelical dating, Genesis can’t have been written any later than around 1406 BC, 40 years after the Exodus, when Moses died. However, earlier Gilgamesh tablets dated to as early as the Third Dynasty of Ur, 2100–2000 BC seem to contain an abbreviated version of the Flood Myth.
Common Origin?
For me, it isn’t worth quibbling about who scooped the story, because the actual event preceded both the Genesis account and all the flood myths in the world—of which there are a great many. A key reason for the existence of any cultural parallelism was that the different cultures shared a common ancestry.
Although writing began to appear as early as 3200 BC, history and legends were mostly propagated by mouth until well after Ur III. Everyone on earth was descended from Noah, and the story would certainly have spread from Babel along with humanity itself.
According to Ussher, the Flood occurred about (circa) 2350 BC and the Tower of Babel c2200 BC. I think those dates may be just a bit off. History records the 1st Dynasty of Egypt beginning c3100 BC. That had to be years after the Flood, and likely years after the Tower. Sargon the Great (probably Nimrod of the Bible) began ruling from Akkad from c2350 BC, and that would necessarily be some years after the Tower dispersion.
Whatever the dates, knowledge of the Flood would certainly have persisted as cultural lore for hundreds or even thousands of years—dinner-table tales passed from generation to generation.
Perhaps as important is the possibility that the immortal “sons/angels of God” that He placed over the scattered nations would always know of the Flood and would have engineered religious observances that exaggerated their own roles in His cosmos. This is a topic that will be foreign to most of you. I wrote about it in detail in Gods and Demons. Here I will just include one relevant passage:
8 When the Most High divided the nations, when he separated the sons of Adam, he set the bounds of the nations according to the number of the angels of God.
9 And his people Jacob became the portion of the Lord, Israel was the line of his inheritance.
—Deuteronomy 32:8–9 LXX-B
I would suggest that, instead of viewing such parallels as evidence that Scripture is mythical, it is more productive to view them as evidence that there may be more truth in the pagan writings than previously realized.
What constitutes a myth?
In a short blog I just released a day or two ago, titled Religion vs. Mythology, I endorsed an Egyptologist’s definition of “mythology” as allegorical stories about primordial events, which aren’t necessarily meant to be believed, but are rather intended to convey a particular worldview.
The Biblical Flood story, whether myth or history, is clearly a polemic (a “controversial argument, especially one refuting or attacking a specific opinion or doctrine”—Webster) against pagan flood mythologies. The ubiquity of the mythologies supports belief that the Flood was real. I see nothing in the Biblical story to make me think it is not historically accurate. I’ve written a number of articles on the subject (see, for example, Fountains of the Deep and Ships, Boats, Floats and Arks).
What about creation stories? Like the Flood stories, they are ubiquitous in the ancient world. We observe a universe, in which we all reside. Obviously, it exists, so that ubiquity is not surprising. I believe in causality. If something happens, including creation, then it was caused. I have way less confidence in the idea that the universe just popped up spontaneously, or that it has simply always existed, either on its own or as a bud on a multiverse that has always existed, than in the idea that it was created.
The pagan creation stories are clearly mythology. Is Genesis 1?
The Egyptian creation myth
In my article Genesis 1:1–5, Day 1, I presented an artist’s conception of the Mesopotamian version of creation and described how it also seems to picture the Genesis 1 account. One way that historians differentiate between “religion” and “mythology” is that religion is meant to be believed in all its detail, while mythology is intended to impart lessons or principles, without requiring slavish belief in the story itself. Though I didn’t word it quite this way, what I suggested was in a sense that Genesis 1 deliberately presents a mythological picture, obvious to Moses’ audience, in order to teach the superiority of the God of Israel over the gods of the pagans. By definition, that constitutes a polemic.
Here, I will go into a bit more detail on the specifics of the Egyptian version.
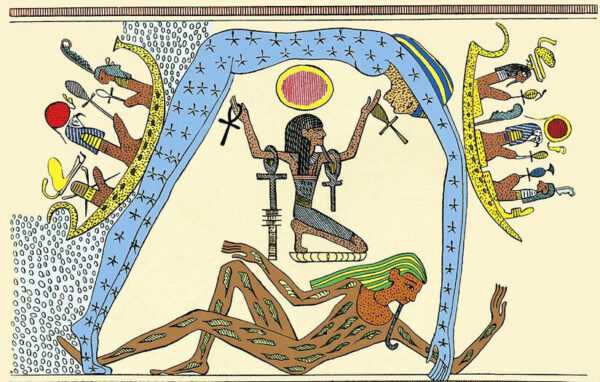
In the beginning, there was the Ogdoad, a group of eight frog-headed “primordial gods”, in four pairs (both brother/sister and husband/wife):
- Hok and Hoket, whose defining attribute was Formlessness.
- Amun and Amunet, whose defining attribute was Invisibility.
- Kuk and Kuket, whose defining attribute was Darkness.
- Nun and Nunet, whose defining attribute was Fluidity.
As a group, the Ogdoad represents a chaotic state, reminiscent of Genesis 1:2 (“without form, and void (or hidden), and darkness on the face of the waters“).
Out of this watery chaos rose a primordial hill, on which stood Atum, from whom all else arose. He created himself and is the father of Shu (air) and Tefnut (moisture).
Shu and Tefnut had two children, Geb (earth) and Nut (sky). This pair is pictured above wearing brown and blue, respectively. In some versions, their father, Shu, is jealous of the incestuous relationship of Geb and Nut and has squeezed himself in between them—”air” between “earth” and “sky.”
Moving beyond the creation of the cosmos, Shu and Tefnut have four children, the pairs Isis and Osiris (the good guys) and Seth (evil) and Nephis (good).
Genesis 1 in the Bible clearly describes the same cosmos as the Egyptian version (and those of other ancient pagan cultures). Clearly, the Bible teaches that the God we worship is Creator of all that exists. To me, that is indisputable. But at the same time, the description presented in Genesis 1 is too much like the pagan myths (but with Yahveh replacing all the pagan gods) and too little like the universe we live in to be taken literally. I would describe it as a polemic against the pagan versions, presented allegorically, like prophetic vision and Jesus’ parables.
The Bible’s use of non-Biblical sources
Still scandalized that the Bible stoops to make use of non-Biblical sources?
In the same way that modern scholarly writers frequently cite earlier sources, so did the Biblical writers. As I mentioned in some detail in Gods and Demons (under “Source Materials”), there are some 100 Biblical references to non-canonical sources actually cited by name by the Scriptural writers. A list can be found on Wikipedia.
Since few of these are now extant, you will often hear them referred to as “lost books of the Bible.” This terminology is unfortunate because it implies that they are inspired works that have somehow slipped through the cracks of history. Not so—I’m pretty sure that if God cared enough to oversee their writing in the first place, He would have protected them from loss.
But what if some of those lost writings were inspired? Then I’m quite comfortable assuming that they were written for a specific time and/or place in history and are no longer relevant. I refuse to waste my energy speculating on possibilities like that since it is all in God’s hand.
Another “but”: If inspired text references other writings, shouldn’t we consider them as inspired as well? Consider the following, for example,
[19] Now the rest of the acts of Jeroboam, how he warred and how he reigned, behold, they are written in the Book of the Chronicles of the Kings of Israel.
—1 Kings 14:19 (ESV)
What this tells me is that the Biblical writers researched their material. It wasn’t merely whispered in their ears by the Holy Spirit. When Christian writers today cite Josephus, they are acknowledging that he was a 1st Century historian who had access to sources that are now unavailable. We believe that Josephus was mostly pretty accurate, so we use what he says where it makes sense, even though we know that (a) he did make occasional demonstrably incorrect statements; and (b) he did write with certain political biases, for a Roman audience. When we cite him without qualification, we are endorsing (at least provisionally) the material applicable to our own work, but not at all the rest of his writings. When a Biblical writer does the same, we aren’t to think that the source material is infallible, just that the Holy Spirit has infallibly endorsed the ideas gleaned from it.
Another use of the term “lost books of the Bible” is in reference to the so-called deuterocanonical (“second canon”) books. These include the apocryphal and pseudepigraphal books found, for example, in Catholic bibles. Also sometimes included are various “gospels” that some folks think should be regarded as canon. They are not “lost” in the sense of being non-extant. All I’ll say about these is that many good books have been written about the selection of Christian canon, and I’m happy to take the position that the Church Fathers did the best possible job in setting the official canon. Though there is much I think can be learned from these sources regarding historical and cultural issues, and common beliefs that were held by ancient peoples, I agree that they cannot be considered inerrant.

The Bible also contains a number of actual quotations from extrabiblical sources like the Book of 1 Enoch. That a non-canonical source was quoted does not mean that the source was Spirit-inspired, only that the Spirit approved the material from that source that was used by the Biblical author. That a passage from 1 Enoch was quoted by Jude and Peter likewise does not imply that the Book of 1 Enoch was inspired; but it does invest the quoted passage with a “seal of authenticity.” In other words, Jude and Peter were inspired in their restating of the quoted words.
I think that we sometimes err in not paying enough attention to such quoted material. Consider, for example,
14 It was also about these that Enoch, the seventh from Adam, prophesied, saying, “Behold, the Lord comes with ten thousands of his holy ones,
15 to execute judgment on all and to convict all the ungodly of all their deeds of ungodliness that they have committed in such an ungodly way, and of all the harsh things that ungodly sinners have spoken against him.”
—Jude 1:14–15 ESV
Jude may be the most underrated book of the Bible. At first glance it seems to have a very simple theme: In times past, and still today, God condemns heresy and wickedness. We are familiar with most of the historical examples of bad behavior given in Jude. Most studies treat them as simple examples of sinful humanity. I think there is way more to it than that. Pending a future blog on the subject, I’m just going to state now that the verses quoted above can’t be understood without also reading the source material, which in this case is still available.
